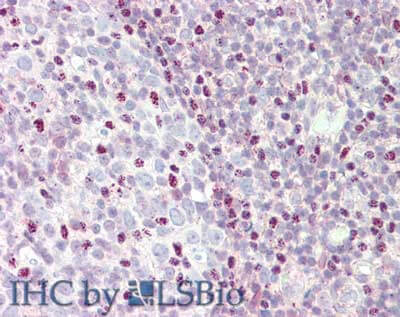
Anti-CTCF (RABBIT) Antibody
CTCF Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND
| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, IHC, E, I, LCI |
| Application Note | CTCF antibody has been tested by ELISA, Immunohistochemistry, and western blotting. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. Expect a band approximately 82.8 kDa or 150 kDa in size corresponding to CTCF by western blotting in the appropriate cell lysate or extract. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Buffer | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Immunogen | CTCF affinity purified antibody was prepared by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to a region near the C-terminus of CTCF protein. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 10664 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 10664 |
| Purity | Anti-CTCF was affinity purified from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity chromatography. This antibody reacts with endogenous CTCF protein. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest reactivity with CTCF from human, mouse, horse, bovine, panda, rabbit, Danio, and chicken based on a 100% homology with the immunizing sequence. Cross-reactivity with CTCF from other sources has not been determined. |
| Storage Condition | Store CTCF antibody at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | CTCF |
|---|---|
| Function | Chromatin binding factor that binds to DNA sequence specific sites and regulates the 3D structure of chromatin (PubMed:18347100, PubMed:18654629, PubMed:19322193). Binds together strands of DNA, thus forming chromatin loops, and anchors DNA to cellular structures, such as the nuclear lamina (PubMed:18347100, PubMed:18654629, PubMed:19322193). Defines the boundaries between active and heterochromatic DNA via binding to chromatin insulators, thereby preventing interaction between promoter and nearby enhancers and silencers (PubMed:18347100, PubMed:18654629, PubMed:19322193). Plays a critical role in the epigenetic regulation (PubMed:16949368). Participates in the allele-specific gene expression at the imprinted IGF2/H19 gene locus (PubMed:16107875, PubMed:16815976, PubMed:17827499). On the maternal allele, binding within the H19 imprinting control region (ICR) mediates maternally inherited higher- order chromatin conformation to restrict enhancer access to IGF2 (By similarity). Mediates interchromosomal association between IGF2/H19 and WSB1/NF1 and may direct distant DNA segments to a common transcription factory (By similarity). Regulates asynchronous replication of IGF2/H19 (By similarity). Plays a critical role in gene silencing over considerable distances in the genome (By similarity). Preferentially interacts with unmethylated DNA, preventing spreading of CpG methylation and maintaining methylation-free zones (PubMed:18413740). Inversely, binding to target sites is prevented by CpG methylation (PubMed:18413740). Plays an important role in chromatin remodeling (PubMed:18413740). Can dimerize when it is bound to different DNA sequences, mediating long-range chromatin looping (PubMed:12191639). Causes local loss of histone acetylation and gain of histone methylation in the beta-globin locus, without affecting transcription (PubMed:12191639). When bound to chromatin, it provides an anchor point for nucleosomes positioning (PubMed:12191639). Seems to be essential for homologous X-chromosome pairing (By similarity). May participate with Tsix in establishing a regulatable epigenetic switch for X chromosome inactivation (PubMed:11743158). May play a role in preventing the propagation of stable methylation at the escape genes from X-inactivation (PubMed:11743158). Involved in sister chromatid cohesion (PubMed:12191639). Associates with both centromeres and chromosomal arms during metaphase and required for cohesin localization to CTCF sites (PubMed:18550811). Plays a role in the recruitment of CENPE to the pericentromeric/centromeric regions of the chromosome during mitosis (PubMed:26321640). Acts as a transcriptional repressor binding to promoters of vertebrate MYC gene and BAG1 gene (PubMed:18413740, PubMed:8649389, PubMed:9591631). Also binds to the PLK and PIM1 promoters (PubMed:12191639). Acts as a transcriptional activator of APP (PubMed:9407128). Regulates APOA1/C3/A4/A5 gene cluster and controls MHC class II gene expression (PubMed:18347100, PubMed:19322193). Plays an essential role in oocyte and preimplantation embryo development by activating or repressing transcription (By similarity). Seems to act as tumor suppressor (PubMed:12191639). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Chromosome. Chromosome, centromere. Note=May translocate to the nucleolus upon cell differentiation. Associates with both centromeres and chromosomal arms during metaphase. Associates with the H19 ICR in mitotic chromosomes. May be preferentially excluded from heterochromatin during interphase |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous. Absent in primary spermatocytes. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Transcriptional repressor CTCF (also known as CCCTC-binding factor) is a transcription factor encoded by the CTCF gene. The CTCF, and the closely related Brother of the Regulator of Imprinted Sites (BORIS), are highly conserved zinc finger proteins implicated in diverse regulatory functions, including transcriptional activation/repression, insulation, imprinting, and X chromosome inactivation. Expression of BORIS is restricted to spermatocytes and is mutually exclusive of CTCF expression. CTCF is ubiquitously expressed in higher eukaryotes and contains a highly conserved and eleven zinc finger central DNA-binding domain, having very high homology between mouse, chicken, and human and is embedded within slightly divergent N and C termini. CTFC plays a critical role in the epigenetic regulation and chromatin remodeling. CTCF has been reported to bind to a variety of DNA target sites that perform distinct functions, including promoter activation or repression, hormone-responsive gene silencing, methylation-dependent chromatin insulation, and genomic imprinting.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.