Anti-p44 MAP Kinase (ERK1) (RABBIT) Antibody
p44 Map Kinase Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Mouse |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, E, IP, I, LCI |
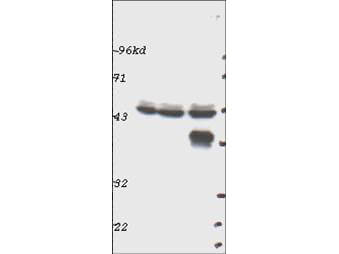
| Application Note | This affinity purified antibody has been tested for use in ELISA, immunoprecipitation and by western blot. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. Expect a predominant band approximately 44 kDa in size corresponding to p44 MAP Kinase (ERK1) by western blotting in the appropriate cell lysate or extract. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Buffer | 0.1 M Tris Chloride, 0.5 M Sodium Chloride, pH 8.0 |
| Immunogen | This affinity purified antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to the carboxy terminal end of human p44 MAP Kinase (ERK1) protein. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 5595 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 5595 |
| Purity | This affinity-purified antibody is directed against the human p44 MAP Kinase (ERK1) protein. The product was affinity purified from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity purification. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest cross reactivity with p44 MAP Kinase (ERK1) proteins from human, bovine, rabbit, rat and mouse. No reactivity is observed against p42 MAP Kinase (ERK2). Reactivity against homologues from other sources is not known. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | MAPK3 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ERK1, PRKM3 |
| Function | Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway (PubMed:34497368). MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade also plays a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, DEPTOR, FRS2 or GRB10) (PubMed:35216969). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substrates which enable the propagation the MAPK/ERK signal to additional cytosolic and nuclear targets, thereby extending the specificity of the cascade. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21708}. Nucleus. Membrane, caveola {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21708}. Cell junction, focal adhesion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63844} Note=Autophosphorylation at Thr-207 promotes nuclear localization (PubMed:19060905). PEA15-binding redirects the biological outcome of MAPK3 kinase-signaling by sequestering MAPK3 into the cytoplasm (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19060905} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Cell proliferation is regulated in several contexts, for example during development, tissue differentiation, wound healing and immune responses. In mammalian cells, proliferative signals lead to the activation of a protein kinase cascade, resulting in the phosphorylation of two closely related Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK’s) ERK1 and ERK2 of 44 kDa and 42 kDa, respectively. When activated, ERK’s form dimers that translocate to the nucleus where they phosphorylate several classes of transcription factors which are involved in the up-regulation of immediate early genes. As such, ERK1 and ERK2 represent a paradigm for a growing family of proline-directed protein kinases that mediate entry, progression and exit from the cell cycle in diverse eukaryotic cells. These enzymes function within highly conserved cascade of sequentially activating protein kinases that transduce signals from diverse extracellular stimuli. Alternative splice transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been described. ERK1 and ERK2 are phosphorylated within the activation loop on both a Threonine and a Tyrosine residue (within a Thr-Glu-Tyr motif) by MEKs (MAPK/ERK kinases), thereby greatly elevating the activity of ERK1&2.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.