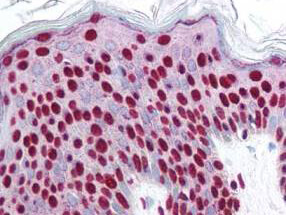
Anti-SMAD3 pS423 pS425 (RABBIT) Antibody
SMAD3 phospho S423/phospho S425 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, IHC, E, I, LCI |
| Application Note | This affinity purified antibody has been tested for use in ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and western blot. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. Expect a band approximately 48 kDa in size corresponding to phosphorylated Smad3 protein by western blotting in the appropriate stimulated tissue or cell lysate or extract. Less than 0.2% reactivity is observed against the non-phosphorylated form of the immunizing peptide. This antibody is phospho specific for dual phosphorylated pS423 and pS425 of Smad3. Stimulation with 2 ng/ml TGF-beta for 1 hour is suggested. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Buffer | 0.02 M Potassium Phosphate, 0.15 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 |
| Immunogen | Anti-SMAD3 pS423pS425 antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a dual phosphorylated synthetic peptide corresponding to a c-terminal region with Serine 423 and Serine 425 of human SMAD3 protein. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 4088 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 4088 |
| Purity | This affinity-purified antibody is directed against the phosphorylated form of human Smad3 protein at the pS423 and pS425 residues. The product was affinity purified from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity purification. Antiserum was first purified against the phosphorylated form of the immunizing peptide. The resultant affinity purified antibody was then cross adsorbed against the non-phosphorylated form of the immunizing peptide. Reactivity occurs against human Smad3 pS423 and pS425 protein and the antibody is specific for the phosphorylated form of the protein. Reactivity with non-phosphorylated human Smad3 is minimal by ELISA and western blot. Expect reactivity against phosphorylated Smad1 and Smad5. Negligible reactivity is seen against other phosphorylated Smad family members. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest cross reactivity with Smad3 from human, Xenopus laevis, Xenopus tropicalis, zebrafish, rat, mouse, swine, bovine and chicken based on 100% sequence homology with the immunogen. Reactivity against homologues from other sources is not known. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | SMAD3 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MADH3 |
| Function | Receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that is an intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinases. Binds the TRE element in the promoter region of many genes that are regulated by TGF-beta and, on formation of the SMAD3/SMAD4 complex, activates transcription. Also can form a SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP- 1/SMAD site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated transcription. Has an inhibitory effect on wound healing probably by modulating both growth and migration of primary keratinocytes and by altering the TGF-mediated chemotaxis of monocytes. This effect on wound healing appears to be hormone-sensitive. Regulator of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis and inhibits early healing of bone fractures. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Cytoplasmic and nuclear in the absence of TGF-beta. On TGF-beta stimulation, migrates to the nucleus when complexed with SMAD4 (PubMed:15799969, PubMed:21145499). Through the action of the phosphatase PPM1A, released from the SMAD2/SMAD4 complex, and exported out of the nucleus by interaction with RANBP1 (PubMed:16751101, PubMed:19289081). Co-localizes with LEMD3 at the nucleus inner membrane (PubMed:15601644). MAPK-mediated phosphorylation appears to have no effect on nuclear import (PubMed:19218245). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236). Localized mainly to the nucleus in the early stages of embryo development with expression becoming evident in the cytoplasm of the inner cell mass at the blastocyst stage (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BUN5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601644, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16751101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19218245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19289081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21145499} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This antibody is designed, produced, and validated as part of a collaboration between Rockland and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and is suitable for Cancer, Immunology and Nuclear Signaling research. Smad3 (also known as Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 Mothers against DPP homolog 3, Mad3, hMAD-3, JV15-2 or hSMAD3) is a transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinase. These activators exert diverse effects on a wide array of cellular processes. The Smad proteins mediate much of the signaling responses induced by the TGF-b superfamily. Briefly, activated type I receptor phosphorylates receptor-activated Smads (R-Smads) at their c-terminal two extreme serines in the SSXS motif, e.g. Smad2 and Smad3 proteins in the TGF-b pathway, or Smad1, Smad5 or Smad8 in the BMP pathway. Then the phosphorylated R-Smad translocated into nucleus, where they regulate transcription of target genes. Based on microarray and animal model experiments, Smad3 accounts for at least 80% of all TGF-b-mediated response.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.