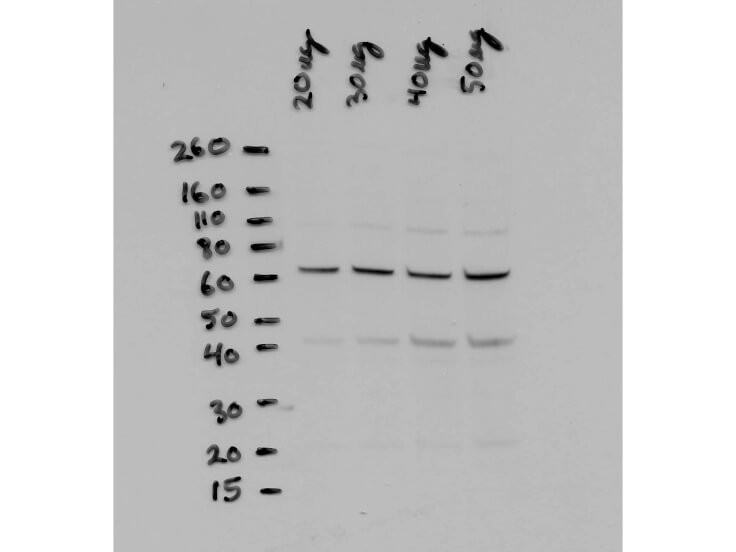
Anti-NFKB p65 (Rel A) N-TERMINAL SPECIFIC (RABBIT) Antibody
NFkB p65 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, E, I, LCI |
| Application Note | Anti-NFkB p65 (N-terminal specific) has been tested for the detection of human NFkB p65 (N-terminal specific) by immunoblot. Functionality in supershift assays has not been determined. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Immunogen | Anti-NFkB p65 Antibody was produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic NFkB p65 peptide corresponding to a region near the N-terminus of the human protein conjugated to Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH). |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 5970 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 5970 |
| Purity | NFkB p65 Antibody was prepared from monospecific antiserum by delipidation and defibrination. Anti-NFkB p65 (N-terminal specific) may react non-specifically with other proteins. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | RELA |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NFKB3 |
| Function | NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain- containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. The NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 and RELA-REL complexes, for instance, function as transcriptional activators. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I- kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The inhibitory effect of I- kappa-B on NF-kappa-B through retention in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with RELA. RELA shows a weak DNA- binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF- kappa-B complex. Beside its activity as a direct transcriptional activator, it is also able to modulate promoters accessibility to transcription factors and thereby indirectly regulate gene expression. Associates with chromatin at the NF-kappa-B promoter region via association with DDX1. Essential for cytokine gene expression in T- cells (PubMed:15790681). The NF-kappa-B homodimeric RELA-RELA complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. Key transcription factor regulating the IFN response during SARS-CoV-2 infection (PubMed:33440148). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B) (PubMed:1493333). Colocalized with DDX1 in the nucleus upon TNF-alpha induction (PubMed:19058135). Colocalizes with GFI1 in the nucleus after LPS stimulation (PubMed:20547752). Translocation to the nucleus is impaired in L.monocytogenes infection (PubMed:20855622) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Anti-NFkB p65 Antibody detects NfkB p65. NFkB-p65 a subunit of NF-kappa-B transcription complex, which plays a crucial role in inflammatory and immune responses. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B upon NF-kappa-B in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. P65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. There are five NFkB proteins in mammals (RelA/NFkB-p65, RelB, c-Rel, NF-_B1/NFkB-p105, and NF-_B2/NFkB-p100). They form a variety of homodimers and heterodimers, each of which activates its own characteristic set of genes. Three splice-variant isoforms have been identified. Anti-NFkB p65 Antibody is ideal for investigators involved in Cell Signaling, Immunology, Cancer, and Signal Transduction research.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.