Anti-COX-2 (RABBIT) Antibody
Cox-2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

| Host | Rabbit |
|---|---|
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Target Species | Human |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
Application
| WB, IHC, E, I, LCI |
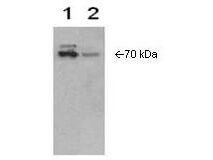
| Application Note | Cox-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) is an inducible enzyme that is normally absent from cells, however, in response to growth factors, tumor promoters and some cytokines, it undergoes a rapid and transient expression. This antiserum against Human Cox-2 and has been tested for use in immunoblotting. The antibody recognizes Cox-2 at 70kDa in Sf9 cell lines transfected with Cox-2 as well as in WISH cells induced with IL-1b. Reactivity in other immunoassays is unknown. |
| Physical State | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Immunogen | This whole rabbit serum was prepared by repeated immunizations with a fusion protein corresponding to the carboxy-terminus of human Cox-2. |
| Preservative | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Gene ID | 5743 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | 5743 |
| Purity | This antiserum is directed against human Cox-2. Two different isoforms of the enzyme are known, Cox-1 and Cox-2. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest cross-reactivity with Cox-2 in human, mouse and rat based on a homology with the immunizing sequence and should not cross react with Cox-1. Reactivity against homologues from other sources is not known. Reactivity of this antibody with Cox-2 from other species is unknown. |
| Storage Condition | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Precautions Note | This product is for research use only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Name | PTGS2 (HGNC:9605) |
|---|---|
| Function | Dual cyclooxygenase and peroxidase in the biosynthesis pathway of prostanoids, a class of C20 oxylipins mainly derived from arachidonate ((5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate, AA, C20:4(n-6)), with a particular role in the inflammatory response (PubMed:11939906, PubMed:16373578, PubMed:19540099, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:7947975, PubMed:9261177). The cyclooxygenase activity oxygenates AA to the hydroperoxy endoperoxide prostaglandin G2 (PGG2), and the peroxidase activity reduces PGG2 to the hydroxy endoperoxide prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), the precursor of all 2-series prostaglandins and thromboxanes (PubMed:16373578, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:7947975, PubMed:9261177). This complex transformation is initiated by abstraction of hydrogen at carbon 13 (with S- stereochemistry), followed by insertion of molecular O2 to form the endoperoxide bridge between carbon 9 and 11 that defines prostaglandins. The insertion of a second molecule of O2 (bis-oxygenase activity) yields a hydroperoxy group in PGG2 that is then reduced to PGH2 by two electrons (PubMed:16373578, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:7947975, PubMed:9261177). Similarly catalyzes successive cyclooxygenation and peroxidation of dihomo-gamma-linoleate (DGLA, C20:3(n-6)) and eicosapentaenoate (EPA, C20:5(n-3)) to corresponding PGH1 and PGH3, the precursors of 1- and 3-series prostaglandins (PubMed:11939906, PubMed:19540099). In an alternative pathway of prostanoid biosynthesis, converts 2-arachidonoyl lysophopholipids to prostanoid lysophopholipids, which are then hydrolyzed by intracellular phospholipases to release free prostanoids (PubMed:27642067). Metabolizes 2-arachidonoyl glycerol yielding the glyceryl ester of PGH2, a process that can contribute to pain response (PubMed:22942274). Generates lipid mediators from n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) via a lipoxygenase-type mechanism. Oxygenates PUFAs to hydroperoxy compounds and then reduces them to corresponding alcohols (PubMed:11034610, PubMed:11192938, PubMed:9048568, PubMed:9261177). Plays a role in the generation of resolution phase interaction products (resolvins) during both sterile and infectious inflammation (PubMed:12391014). Metabolizes docosahexaenoate (DHA, C22:6(n-3)) to 17R-HDHA, a precursor of the D-series resolvins (RvDs) (PubMed:12391014). As a component of the biosynthetic pathway of E- series resolvins (RvEs), converts eicosapentaenoate (EPA, C20:5(n-3)) primarily to 18S-HEPE that is further metabolized by ALOX5 and LTA4H to generate 18S-RvE1 and 18S-RvE2 (PubMed:21206090). In vascular endothelial cells, converts docosapentaenoate (DPA, C22:5(n-3)) to 13R- HDPA, a precursor for 13-series resolvins (RvTs) shown to activate macrophage phagocytosis during bacterial infection (PubMed:26236990). In activated leukocytes, contributes to oxygenation of hydroxyeicosatetraenoates (HETE) to diHETES (5,15-diHETE and 5,11- diHETE) (PubMed:22068350, PubMed:26282205). Can also use linoleate (LA, (9Z,12Z)-octadecadienoate, C18:2(n-6)) as substrate and produce hydroxyoctadecadienoates (HODEs) in a regio- and stereospecific manner, being (9R)-HODE ((9R)-hydroxy-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoate) and (13S)- HODE ((13S)-hydroxy-(9Z,11E)-octadecadienoate) its major products (By similarity). During neuroinflammation, plays a role in neuronal secretion of specialized preresolving mediators (SPMs) 15R-lipoxin A4 that regulates phagocytic microglia (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Microsome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Nucleus inner membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Nucleus outer membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Note=Detected on the lumenal side of the endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
COX-2, also known as prostaglandin H synthase, was identified less than a decade ago. Its discovery was followed by a period of discovery and drug development to create a “super aspirin” and led to insights into arthritis, Alzheimer's disease, colorectal cancer and regulation of brain and kidney function in search of better treatments for degenerative and inflammatory diseases. Cox-2 is involved in the response of cells to growth factors, tumor promoters, and cytokines that induce its expression. Given its role in synthesizing prostaglandins, Cox-2 is therefore of interest in studying immune response regulation.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.