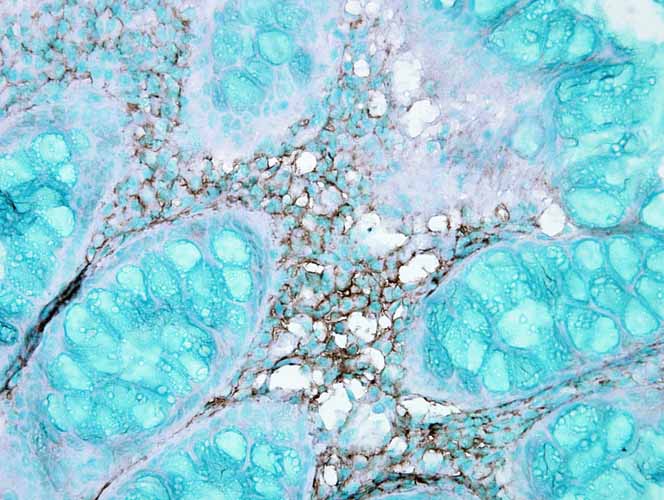
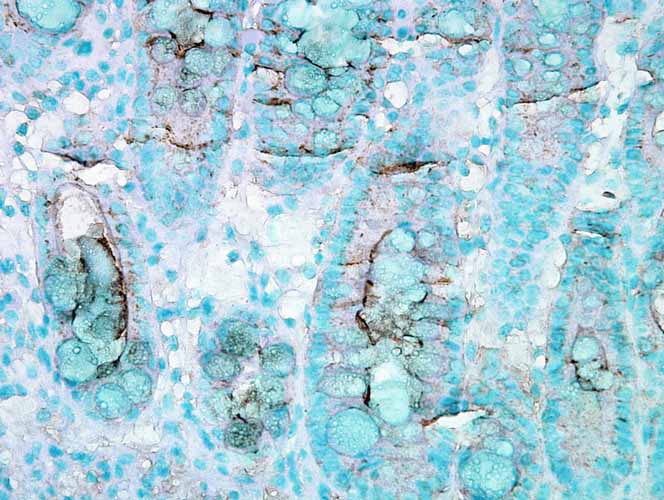
HSC70 (HSP73) Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, IP, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P11142 |
| Other Accession | NP_006588.1 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Description | Rabbit Anti-Human HSC70 (HSP73) Polyclonal |
| Target/Specificity | Detects 73kDa. Does not cross-react with HSP70. |
| Other Names | HSC54 Antibody, HSC71 Antibody, HSC73 Antibody, HSP71 Antibody, HSP73 Antibody, HSPA10 Antibody, HSPA8 Antibody, LAP1 Antibody, NIP71 Antibody |
| Immunogen | Amino acids 650-670 of human HSP73 |
| Purification | Rabbit Antiserum |
| Storage | 4ºC |
| Storage Buffer | Rabbit Antiserum |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Certificate of Analysis | 0.5 µg/ml of SPC-102 was sufficient for detection of HSC70 20 µg of heat shocked HeLa cell lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat anti-rabbit IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm | Melanosome |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
HSP70 genes encode abundant heat-inducible 70-kDa HSPs (HSP70s). In most eukaryotes HSP70 genes exist as part of a multigene family. They are found in most cellular compartments of eukaryotes including nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum and the cytosol, as well as in bacteria. The genes show a high degree of conservation, having at least 50% identity (2). The N-terminal two thirds of HSP70s are more conserved than the C-terminal third. HSP70 binds ATP with high affinity and possesses a weak ATPase activity which can be stimulated by binding to unfolded proteins and synthetic peptides (3). When HSC70 (constitutively expressed) present in mammalian cells was truncated, ATP binding activity was found to reside in an N-terminal fragment of 44 kDa which lacked peptide binding capacity. Polypeptide binding ability therefore resided within the C-terminal half (4). The structure of this ATP binding domain displays multiple features of nucleotide binding proteins (5). When cells are subjected to metabolic stress (e.g. heat shock) a member of the HSP 70 family, HSP 70 (HSP72), is expressed; HSP 70 is highly related to HSC70 (>90% sequence identity). Constitutively expressed HSC70 rapidly forms a stable complex with the highly inducible HSP70 in cells following heat shock. The interaction of HSC70 with HSP 70 is regulated by ATP. These two heat shock proteins move together in the cell experiencing stress. Furthermore, research on HSC70 has implicates it with a role in facilitating the recovery of centrosomal structure and function after heat shock (6).
References
1. Brown C.L. et al. (1993) J.Cell Biol., 120 (5): 1101-1112.
2. Boorstein W.R., Ziegelhoffer T., and Craig E.A. (1993) J. Mol. Evol. 38(1): 1-17.
3. Rothman J. (1989), Cell 59: 591-601.
4. DeLuca-Flaherty et al. (1990) Cell 62: 875-887.
5. Bork P., Sander C., and Valencia A. (1992) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89: 7290-7294.
6. Brown C.L. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271(2): 833-840.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.