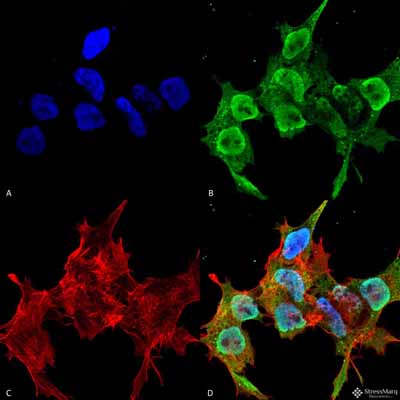
Synaptotagmin-12 Antibody
Synaptotagmin 12 Antibody, Clone S277-7
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q920N7 |
| Other Accession | NP_598925.1 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Description | Mouse Anti-Mouse Synaptotagmin-12 Monoclonal IgG1 |
| Target/Specificity | Detects ~45kDa. Does not cross-react with Synaptotagmin-6 or other Synaptotagmins. |
| Other Names | SYT-12 Antibody, SYT12 Antibody, Synaptotagmin 12 Antibody, Synaptotagmin XII Antibody, SytXII Antibody, Syt XII Antibody, Synaptotagmin12 Antibody, SynaptotagminXII Antibody |
| Clone Names | S277-7 |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein amino acids 168-255 (Cytoplasmic C2A domain) of mouse Synaptotagmin-12 |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Storage | -20ºC |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Shipping Temperature | Blue Ice or 4ºC |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 µg/ml of SMC-437 was sufficient for detection of Synaptotagmin-12 in 20 µg of transiently overexpressing synaptotagmin-12 COS cell lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasmic Vesicle |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Synaptotagmins constitute a family of membrane trafficking proteins that are characterized by an N-terminal transmembrane region (TMR), a variable linker, and two C-terminal C2 domains - C2A and C2B. There are 15 members in the mammalian synaptotagmin family. There are several C2-domain containing protein families that are related to synaptotagmins, including transmembrane (Ferlins, E-Syts, and MCTPs) and soluble (RIMs, Munc13s, synaptotagmin-related proteins and B/K) proteins. The synaptotagmins are integral membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles thought to serve as Ca(2+) sensors in the process of vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. Calcium binding to synaptotagmin participates in triggering neurotransmitter release at the synapse. The first domain mediates Ca(2+)-dependent phospholipid binding. The second C2 domain mediates interaction with Stonin 2. Synaptotagmin may have a regulatory role in the membrane interactions during trafficking of synaptic vesicles at the active zone of the synapse. It binds acidic phospholipids with a specificity that requires the presence of both an acidic head group and a diacyl backbone. A Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between synaptotagmin and putative receptors for activated protein kinase C has also been reported. It can bind to at least three additional proteins in a Ca(2+)-independent manner; these are neurexins, syntaxin and AP2 (1, 2).
References
1. Schengrund C.L., et al. (2002) J Biol Chem. 277: 32815.
2. Reichardt L.F., et al. (1981) J Cell Biol. 91:257.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.