Blimp-1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O75626 |
| Other Accession | NP_001189, 172072684 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 91771 Da |
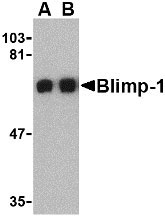
| Application Notes | Blimp-1 antibody can be used for detection of Blimp-1 by Western blot at 0.5 - 1 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunoflourescence starting at 20 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 639 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Blimp-1 Antibody: BLIMP1, PRDI-BF1, BLIMP1, PR domain zinc finger protein 1, BLIMP-1, PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain |
| Target/Specificity | PRDM1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Blimp-1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | Blimp-1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PRDM1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BLIMP1 |
| Function | Transcription factor that mediates a transcriptional program in various innate and adaptive immune tissue-resident lymphocyte T cell types such as tissue-resident memory T (Trm), natural killer (trNK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells and negatively regulates gene expression of proteins that promote the egress of tissue-resident T-cell populations from non-lymphoid organs. Plays a role in the development, retention and long-term establishment of adaptive and innate tissue- resident lymphocyte T cell types in non-lymphoid organs, such as the skin and gut, but also in other nonbarrier tissues like liver and kidney, and therefore may provide immediate immunological protection against reactivating infections or viral reinfection (By similarity). Binds specifically to the PRDI element in the promoter of the beta- interferon gene (PubMed:1851123). Drives the maturation of B- lymphocytes into Ig secreting cells (PubMed:12626569). Associates with the transcriptional repressor ZNF683 to chromatin at gene promoter regions (By similarity). Binds to the promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor of IRF8, thereby promotes transcription of osteoclast differentiation factors such as NFATC1 and EEIG1 (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Blimp-1 Antibody: Blimp-1 was initially identified as a zinc finger-containing protein that drives the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Together with X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1), Blimp-1 is induced upon terminal differentiation of plasma cells. The transcriptional repressor activity of Blimp-1 has also been found to regulate T cell homeostasis and function, possibly by suppressing the expression of the cytokines IL-2 and interferon-gamma during T cell development. More recent experiments have suggested that Blimp-1 also plays a major role in the formation of primordial germ cells (PGC) in developing mammalian embryos. In these experiments, Blimp-1-deficient mutant mouse embryos form a cluster of PGC-like cells which fail to show the expected migration, proliferation, and repression of homeobox genes that normally accompany specification of primordial germ cells.
References
Turner CAJ, Mack DH, and Davis MM. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B-lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell 1994; 77:297-306.
Angelin-Duclos C, Cattoretti G, Lin K-I, et al. Commitment of B lymphocytes to a plasma cell fate is associated with Blimp-1 expression. J. Immunol. 2000; 165:5462-71.
Reimold AM, Iwakoshi NN, Manis J, et al. Plasma cell differentiation requires the transcription factor XBP-1. Nature 2001; 412:300-7.
Martins GA, Cimmino L, Shapiro-Shelef M, et al. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function. Nature Immunol. 2006; 7:457-65.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.