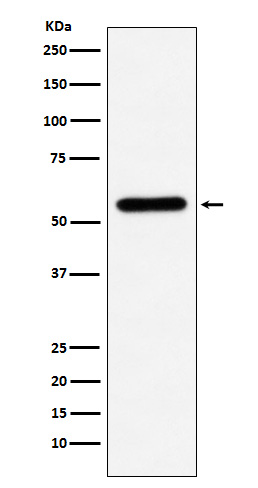
Liver Carboxylesterase 1 Antibody
Rabbit mAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, IP |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P23141 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Other Names | ACAT; CE 1; CEH; CES1; CES2; CESDD1; Egasyn; ES-HTEL; ES-x; Es22; Esterase 22; hCE 1; HMSE; HMSE1; REH; SES1; TGH; Triacylglycerol hydrolase; |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Calculated MW | 62521 Da |
| Dilution | WB 1:1000~1:5000 IP 1:40 FC 1:100 |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Liver Carboxylesterase 1 |
| Description | Involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics and in the activation of ester and amide prodrugs. Hydrolyzes aromatic and aliphatic esters, but has no catalytic activity toward amides or a fatty acyl-CoA ester. Hydrolyzes the methyl ester group of cocaine to form benzoylecgonine. |
| Storage Condition and Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Name | CES1 (HGNC:1863) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CES2, SES1 |
| Function | Involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics and in the activation of ester and amide prodrugs (PubMed:18762277, PubMed:7980644, PubMed:9169443, PubMed:9490062). Hydrolyzes aromatic and aliphatic esters, but has no catalytic activity toward amides or a fatty acyl-CoA ester (PubMed:18762277, PubMed:7980644, PubMed:9169443, PubMed:9490062). Hydrolyzes the methyl ester group of cocaine to form benzoylecgonine (PubMed:7980644). Catalyzes the transesterification of cocaine to form cocaethylene (PubMed:7980644). Displays fatty acid ethyl ester synthase activity, catalyzing the ethyl esterification of oleic acid to ethyloleate (PubMed:7980644). Converts monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. Hydrolyzes of 2-arachidonoylglycerol and prostaglandins (PubMed:21049984). Hydrolyzes cellular cholesteryl esters to free cholesterols and promotes reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) by facilitating both the initial and final steps in the process (PubMed:11015575, PubMed:16024911, PubMed:16971496, PubMed:18762277). First of all, allows free cholesterol efflux from macrophages to extracellular cholesterol acceptors and secondly, releases free cholesterol from lipoprotein-delivered cholesteryl esters in the liver for bile acid synthesis or direct secretion into the bile (PubMed:16971496, PubMed:18599737, PubMed:18762277). |
| Cellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Cytoplasm Lipid droplet. Note=Moves from cytoplasm to lipid droplets upon lipid loading. Associates with lipid droplets independently of triglycerides (TG) content of the droplets and hydrolyzes cholesteryl esters more efficiently from mixed droplets |
| Tissue Location | Expressed predominantly in liver with lower levels in heart and lung (PubMed:10562416). Expressed in macrophages (PubMed:11015575, PubMed:18762277, PubMed:21049984) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.