RAB7 Antibody (C-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
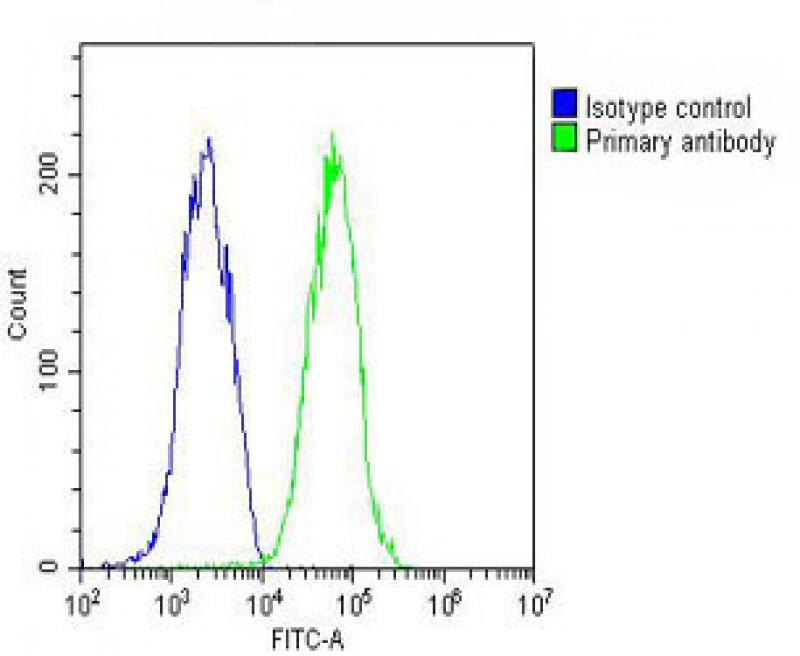
| WB, FC, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P51149 |
| Other Accession | P51150 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 23490 Da |
| Antigen Region | 176-204 aa |
| Gene ID | 7879 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Ras-related protein Rab-7a, RAB7A, RAB7 |
| Target/Specificity | This RAB7 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 176-204 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human RAB7. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 IHC-P~~1:25 FC~~1:25 |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | RAB7 Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | RAB7A (HGNC:9788) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | RAB7 |
| Function | Small GTPase which cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins playing a key role in the regulation of endo- lysosomal trafficking. Governs early-to-late endosomal maturation, microtubule minus-end as well as plus-end directed endosomal migration and positioning, and endosome-lysosome transport through different protein-protein interaction cascades. Plays a central role, not only in endosomal traffic, but also in many other cellular and physiological events, such as growth-factor-mediated cell signaling, nutrient- transportor mediated nutrient uptake, neurotrophin transport in the axons of neurons and lipid metabolism. Also involved in regulation of some specialized endosomal membrane trafficking, such as maturation of melanosomes, pathogen-induced phagosomes (or vacuoles) and autophagosomes. Plays a role in the maturation and acidification of phagosomes that engulf pathogens, such as S.aureus and M.tuberculosis. Plays a role in the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. Plays important roles in microbial pathogen infection and survival, as well as in participating in the life cycle of viruses. Microbial pathogens possess survival strategies governed by RAB7A, sometimes by employing RAB7A function (e.g. Salmonella) and sometimes by excluding RAB7A function (e.g. Mycobacterium). In concert with RAC1, plays a role in regulating the formation of RBs (ruffled borders) in osteoclasts. Controls the endosomal trafficking and neurite outgrowth signaling of NTRK1/TRKA (PubMed:11179213, PubMed:12944476, PubMed:14617358, PubMed:20028791, PubMed:21255211). Regulates the endocytic trafficking of the EGF-EGFR complex by regulating its lysosomal degradation. Involved in the ADRB2-stimulated lipolysis through lipophagy, a cytosolic lipase-independent autophagic pathway (By similarity). Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). Required for vesicular trafficking and cell surface expression of ACE2 (PubMed:33147445). May play a role in PRPH neuronal intermediate filament assembly (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle, phagosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Late endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Melanosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Lipid droplet {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51150}. Endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51150} Mitochondrion membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Note=Colocalizes with OSBPL1A at the late endosome (PubMed:16176980). Found in the ruffled border (a late endosomal-like compartment in the plasma membrane) of bone-resorbing osteoclasts. Recruited to phagosomes containing S.aureus or Mycobacterium (PubMed:21255211). Lipid droplet localization is increased upon ADRB2 stimulation (By similarity). Recruited to damaged mitochondria during mitophagy in a RIMOC1-dependent manner (PubMed:34432599). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16176980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21255211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34432599} |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed; high expression found in skeletal muscle. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
RAB family members are small, RAS-related GTP-binding proteins that are important regulators of vesicular transport. Each RAB protein targets multiple proteins that act in exocytic / endocytic pathways. RAB7 is a RAB family member that regulates vesicle traffic in the late endosomes and also from late endosomes to lysosomes. This protein is also involved in the cellular vacuolation of the VacA cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori.
References
Davies,J.P., et.al., Genomics 41 (1), 131-134 (1997)
Vitelli,R., et.al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 229 (3), 887-890 (1996)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.