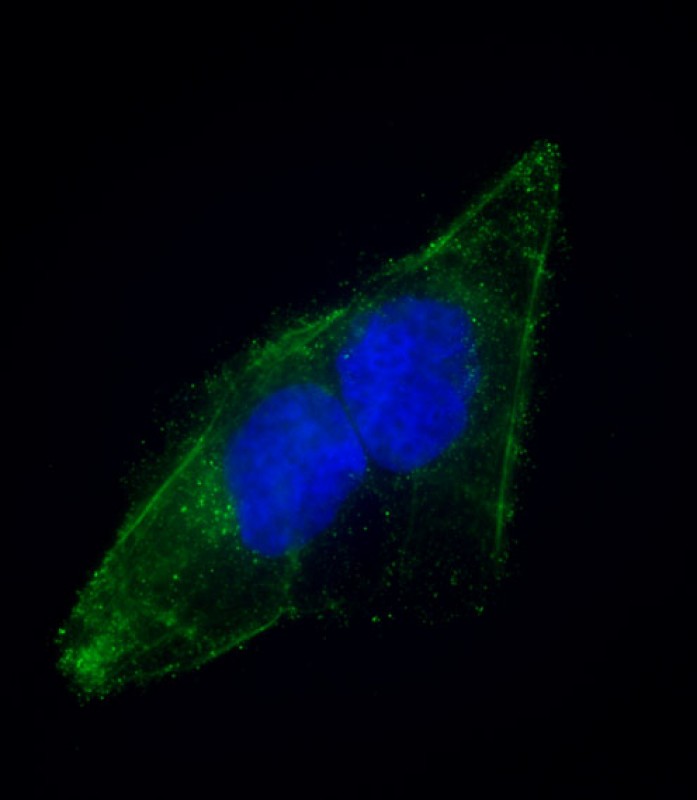
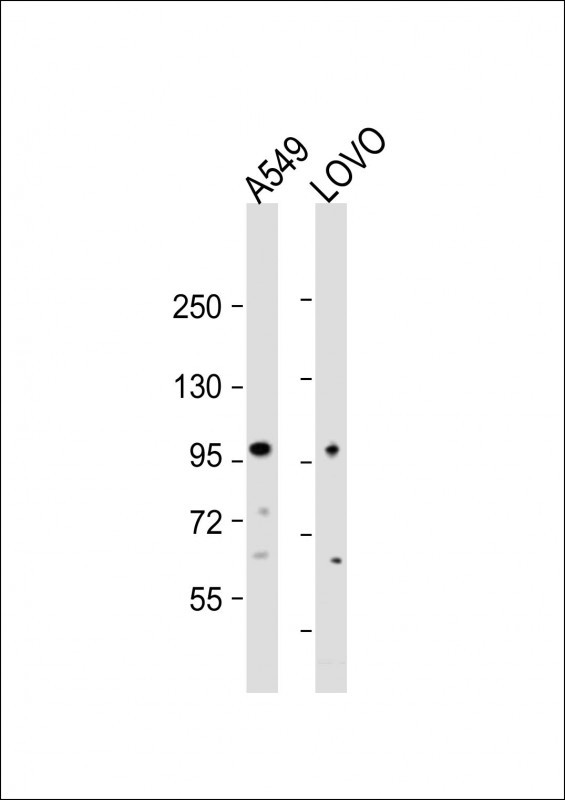
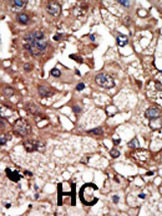
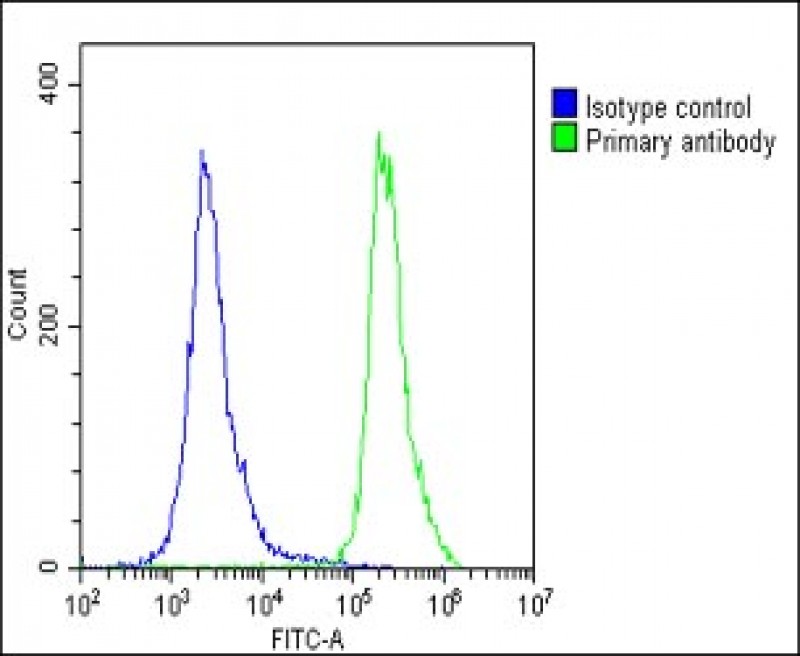
EPS8 Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC-P, WB, FC, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q12929 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 91882 Da |
| Antigen Region | 9-39 aa |
| Gene ID | 2059 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8, EPS8 |
| Target/Specificity | This EPS8 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 9-39 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human EPS8. |
| Dilution | IF~~1:25 WB~~1:500 IHC-P~~1:50~100 FC~~1:25 |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | EPS8 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | EPS8 |
|---|---|
| Function | Signaling adapter that controls various cellular protrusions by regulating actin cytoskeleton dynamics and architecture. Depending on its association with other signal transducers, can regulate different processes. Together with SOS1 and ABI1, forms a trimeric complex that participates in transduction of signals from Ras to Rac by activating the Rac-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity. Acts as a direct regulator of actin dynamics by binding actin filaments and has both barbed-end actin filament capping and actin bundling activities depending on the context. Displays barbed-end actin capping activity when associated with ABI1, thereby regulating actin- based motility process: capping activity is auto-inhibited and inhibition is relieved upon ABI1 interaction. Also shows actin bundling activity when associated with BAIAP2, enhancing BAIAP2-dependent membrane extensions and promoting filopodial protrusions. Involved in the regulation of processes such as axonal filopodia growth, stereocilia length, dendritic cell migration and cancer cell migration and invasion. Acts as a regulator of axonal filopodia formation in neurons: in the absence of neurotrophic factors, negatively regulates axonal filopodia formation via actin-capping activity. In contrast, it is phosphorylated in the presence of BDNF leading to inhibition of its actin-capping activity and stimulation of filopodia formation. Component of a complex with WHRN and MYO15A that localizes at stereocilia tips and is required for elongation of the stereocilia actin core. Indirectly involved in cell cycle progression; its degradation following ubiquitination being required during G2 phase to promote cell shape changes. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cell projection, ruffle membrane. Cell projection, growth cone. Cell projection, stereocilium {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08509}. Synapse, synaptosome Note=Localizes at the tips of the stereocilia of the inner and outer hair cells (By similarity). Localizes to the midzone of dividing cells {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08509} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in all tissues analyzed, including heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas Expressed in all epithelial and fibroblastic lines examined and in some, but not all, hematopoietic cells |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Upon binding to EGF receptor, EPS8 enhances EGF-dependent mitogenic signals. It can bind multiple cellular targets. EPS8 is expressed in all tissues analyzed, including heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, and pancreas. It is expressed in all epithelial and fibroblastic lines examined and in some, but not all, hematopoietic cells. EPS8 is phosphorylated by several receptor tyrosine kinases. The protein contains 1 PH domain and 1 SH3 domain.
References
Wong, W.T., et al., Oncogene 9(10):3057-3061 (1994).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.















 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.