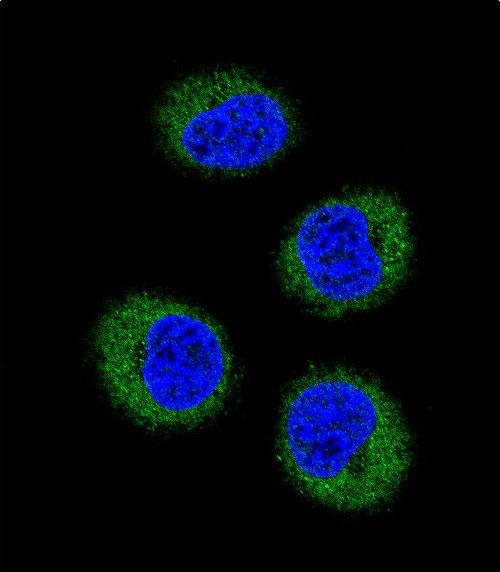
FGR Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 2
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IF, IHC-P, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P09769 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 59479 Da |
| Antigen Region | 3-33 aa |
| Gene ID | 2268 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr, Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma viral (v-fgr) oncogene homolog, Proto-oncogene c-Fgr, p55-Fgr, p58-Fgr, p58c-Fgr, FGR, SRC2 |
| Target/Specificity | This FGR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 3-33 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human FGR. |
| Dilution | IF~~1:10~50 WB~~1:2000 IHC-P~~1:50~100 |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FGR Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FGR |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SRC2 |
| Function | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that transmits signals from cell surface receptors devoid of kinase activity and contributes to the regulation of immune responses, including neutrophil, monocyte, macrophage and mast cell functions, cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, phagocytosis, cell adhesion and migration. Promotes mast cell degranulation, release of inflammatory cytokines and IgE-mediated anaphylaxis. Acts downstream of receptors that bind the Fc region of immunoglobulins, such as MS4A2/FCER1B, FCGR2A and/or FCGR2B. Acts downstream of ITGB1 and ITGB2, and regulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell spreading and adhesion. Depending on the context, activates or inhibits cellular responses. Functions as a negative regulator of ITGB2 signaling, phagocytosis and SYK activity in monocytes. Required for normal ITGB1 and ITGB2 signaling, normal cell spreading and adhesion in neutrophils and macrophages. Functions as a positive regulator of cell migration and regulates cytoskeleton reorganization via RAC1 activation. Phosphorylates SYK (in vitro) and promotes SYK-dependent activation of AKT1 and MAP kinase signaling. Phosphorylates PLD2 in antigen-stimulated mast cells, leading to PLD2 activation and the production of the signaling molecules lysophosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol. Promotes activation of PIK3R1. Phosphorylates FASLG, and thereby regulates its ubiquitination and subsequent internalization. Phosphorylates ABL1. Promotes phosphorylation of CBL, CTTN, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1, PTK2B/PYK2 and VAV2. Phosphorylates HCLS1 that has already been phosphorylated by SYK, but not unphosphorylated HCLS1. Together with CLNK, it acts as a negative regulator of natural killer cell-activating receptors and inhibits interferon-gamma production (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor; Cytoplasmic side. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell projection, ruffle membrane. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Mitochondrion inner membrane. Mitochondrion intermembrane space. Note=Detected in mitochondrial intermembrane space and at inner membranes (By similarity). Colocalizes with actin fibers at membrane ruffles. Detected at plasma membrane lipid rafts |
| Tissue Location | Detected in neutrophils, monocytes and natural killer cells (at protein level). Detected in monocytes and large lymphocytes. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
FGR is a member of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). This protein contains N-terminal sites for myristylation and palmitylation, a PTK domain, and SH2 and SH3 domains which are involved in mediating protein-protein interactions with phosphotyrosine-containing and proline-rich motifs, respectively. It localizes to plasma membrane ruffles, and functions as a negative regulator of cell migration and adhesion triggered by the beta-2 integrin signal transduction pathway. Infection with Epstein-Barr virus results in the overexpression of this protein.
References
Carriero, M.V., et al., Biol. Chem. 383(1):107-113 (2002).
Katamine, S., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 8(1):259-266 (1988).
Nishizawa, M., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 6(2):511-517 (1986).
Cheah, M.S., et al., Nature 319(6050):238-240 (1986).
Tronick, S.R., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82(19):6595-6599 (1985).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.















 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.