BAP1 Rabbit mAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

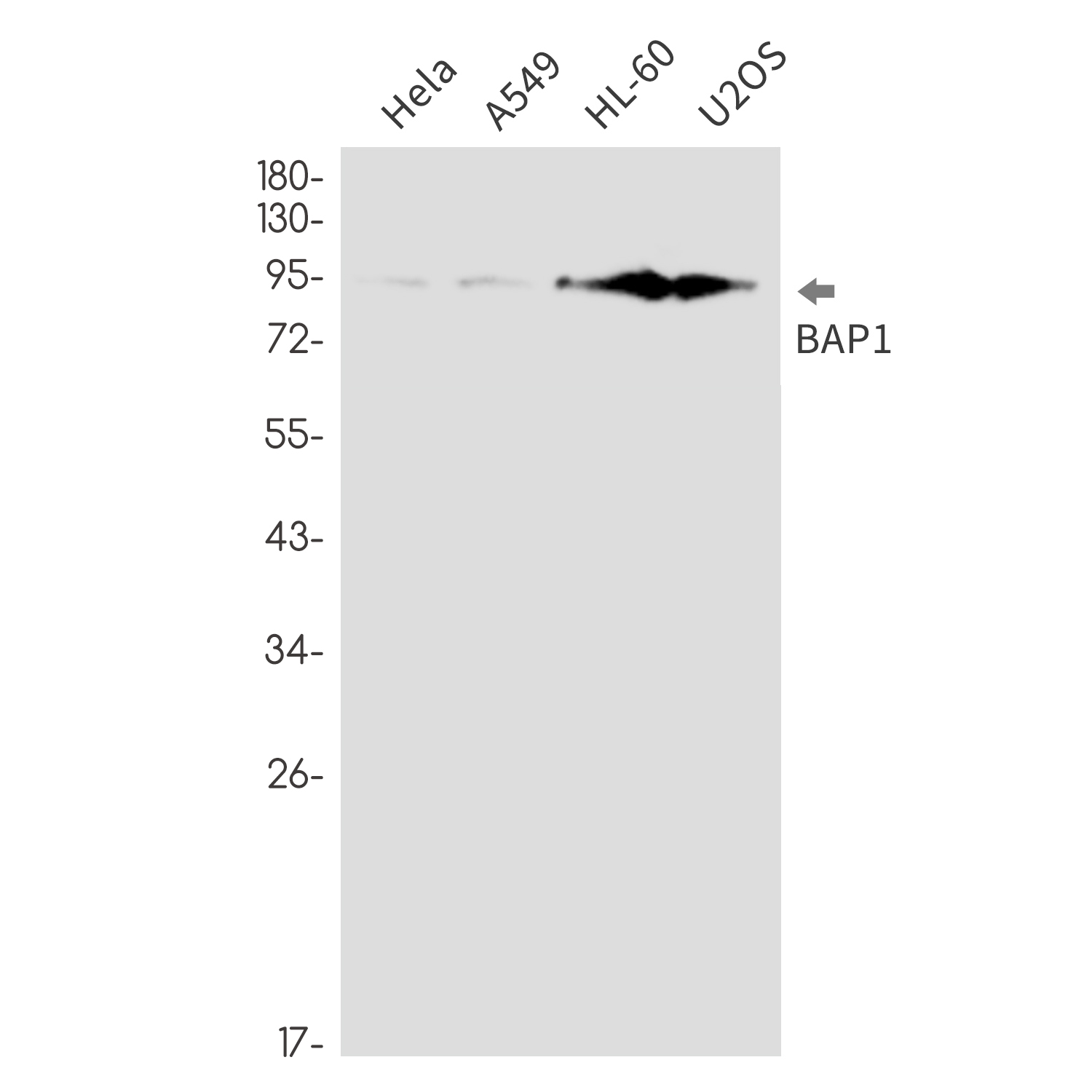
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92560 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Calculated MW | 80362 Da |
| Gene ID | 8314 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | BAP1 |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500-1/1000 |
| Format | Liquid |
| Name | BAP1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9528852, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:950} |
|---|---|
| Function | Deubiquitinating enzyme that plays a key role in chromatin by mediating deubiquitination of histone H2A and HCFC1 (PubMed:12485996, PubMed:18757409, PubMed:20436459, PubMed:25451922, PubMed:35051358). Catalytic component of the polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex, a complex that specifically mediates deubiquitination of histone H2A monoubiquitinated at 'Lys-120' (H2AK119ub1) (PubMed:20436459, PubMed:25451922, PubMed:30664650, PubMed:35051358). Does not deubiquitinate monoubiquitinated histone H2B (PubMed:20436459, PubMed:30664650). The PR-DUB complex is an epigenetic regulator of gene expression and acts as a transcriptional coactivator, affecting genes involved in development, cell communication, signaling, cell proliferation and cell viability (PubMed:20805357, PubMed:30664650, PubMed:36180891). Antagonizes PRC1 mediated H2AK119ub1 monoubiquitination (PubMed:30664650). As part of the PR-DUB complex, associates with chromatin enriched in histone marks H3K4me1, H3K4me3, and H3K27Ac, but not in H3K27me3 (PubMed:36180891). Recruited to specific gene-regulatory regions by YY1 (PubMed:20805357). Acts as a regulator of cell growth by mediating deubiquitination of HCFC1 N- terminal and C-terminal chains, with some specificity toward 'Lys-48'- linked polyubiquitin chains compared to 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains (PubMed:19188440, PubMed:19815555). Deubiquitination of HCFC1 does not lead to increase stability of HCFC1 (PubMed:19188440, PubMed:19815555). Interferes with the BRCA1 and BARD1 heterodimer activity by inhibiting their ability to mediate ubiquitination and autoubiquitination (PubMed:19117993). It however does not mediate deubiquitination of BRCA1 and BARD1 (PubMed:19117993). Able to mediate autodeubiquitination via intramolecular interactions to counteract monoubiquitination at the nuclear localization signal (NLS), thereby protecting it from cytoplasmic sequestration (PubMed:24703950). Negatively regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of trophoblast stem cells during placental development by regulating genes involved in epithelial cell integrity, cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization (PubMed:34170818). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Chromosome. Note=Mainly nuclear (PubMed:24703950, PubMed:30664650). Binds to chromatin (PubMed:30664650). Localizes to the cytoplasm when monoubiquitinated by the E2/E3 hybrid ubiquitin- protein ligase UBE2O (PubMed:24703950). Recruitment to chromatin is dependent on ASXL1/2/3 and recruitment to specific genes on FOXK1/2 (By similarity). Nuclear localization is redundantly mediated by the importin and transportin systems; TNPO1/transportin-1 is the major mediator of nuclear localization (PubMed:35446349) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PU7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30664650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35446349} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in testis, placenta and ovary (PubMed:9528852). Expressed in breast (PubMed:9528852). levels in the placenta increase over the course of pregnancy (PubMed:34170818) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.