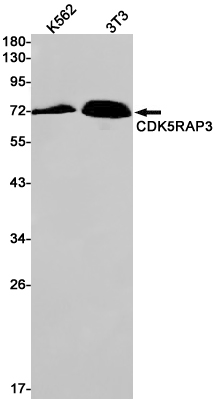
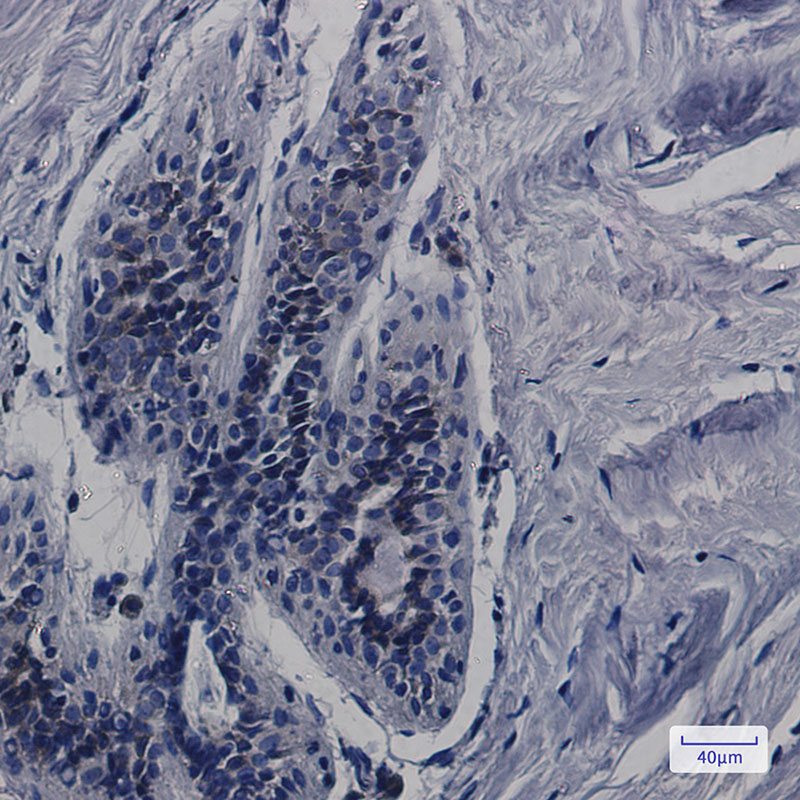
CDK5RAP3 Rabbit mAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IP |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96JB5 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Calculated MW | 56921 Da |
| Gene ID | 80279 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CDK5RAP3 |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500-1/1000 IHC~~1/50-1/100 |
| Format | Liquid |
| Name | CDK5RAP3 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:30635284, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:18673} |
|---|---|
| Function | Substrate adapter of E3 ligase complexes mediating ufmylation, the covalent attachment of the ubiquitin-like modifier UFM1 to substrate proteins, and which is involved in various processes, such as ribosome recycling and reticulophagy (also called ER-phagy) (PubMed:23152784, PubMed:30635284, PubMed:32851973, PubMed:36121123, PubMed:36543799, PubMed:37595036, PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). As part of the UREL complex, plays a key role in ribosome recycling by promoting mono-ufmylation of RPL26/uL24 subunit of the 60S ribosome (PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). Ufmylation of RPL26/uL24 occurs on free 60S ribosomes following ribosome dissociation: it weakens the junction between post-termination 60S subunits and SEC61 translocons, promoting release and recycling of the large ribosomal subunit from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). Ufmylation of RPL26/uL24 and subsequent 60S ribosome recycling either take place after normal termination of translation or after ribosome stalling during cotranslational translocation at the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:32851973, PubMed:37595036, PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). Within the UREL complex, CDK5RAP3 acts as a substrate adapter that constrains UFL1 ligase activity to mono-ufmylate RPL26/uL24 at 'Lys-134' (PubMed:36121123, PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). The UREL complex is also involved in reticulophagy in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress by promoting ufmylation of proteins such as CYB5R3, thereby promoting lysosomal degradation of ufmylated proteins (PubMed:36543799). Also acts as a regulator of transcription: negatively regulates NF-kappa-B-mediated gene transcription through the control of RELA phosphorylation (PubMed:17785205, PubMed:20228063). Also regulates mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint and mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint (PubMed:15790566, PubMed:19223857). Through its interaction with CDKN2A/ARF and MDM2 may induce MDM2-dependent p53/TP53 ubiquitination, stabilization and activation in the nucleus, thereby promoting G1 cell cycle arrest and inhibition of cell proliferation (PubMed:16173922). May also play a role in the rupture of the nuclear envelope during apoptosis (PubMed:23478299). May regulate MAPK14 activity by regulating its dephosphorylation by PPM1D/WIP1 (PubMed:21283629). Required for liver development (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Note=Tethered to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane as part of the UFM1 ribosome E3 ligase (UREL) complex (PubMed:38383785, PubMed:38383789). Colocalizes and associates with microtubules (PubMed:23478299) |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed (PubMed:10721722, PubMed:12054757). Expressed in heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas. Isoform 3 is expressed in kidney, liver, skeletal muscle and placenta (PubMed:12737517) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.