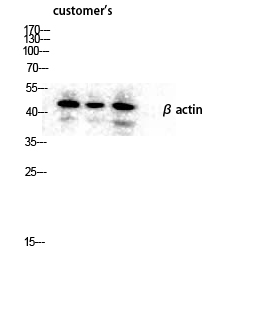
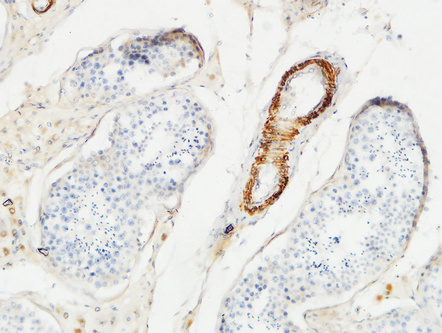
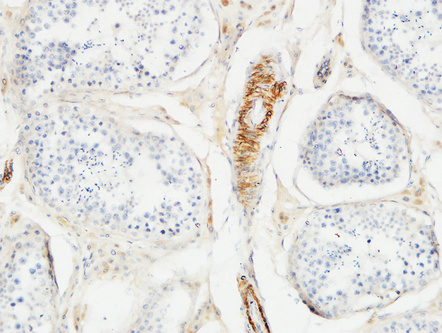
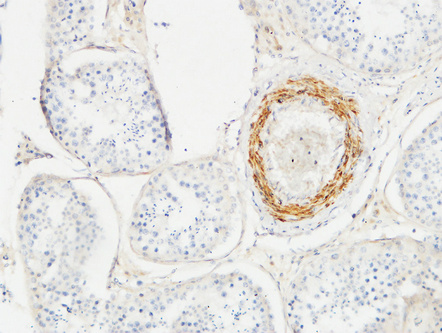
Actin β Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

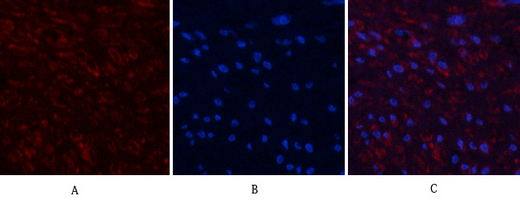
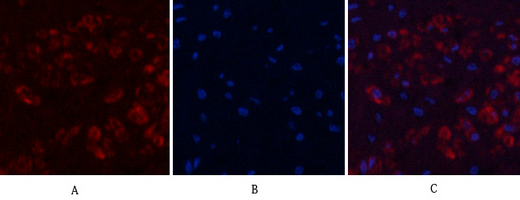
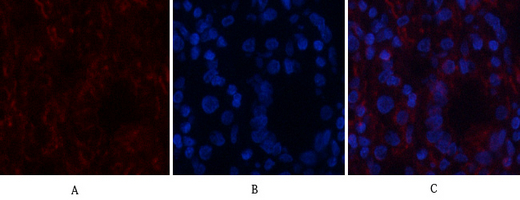
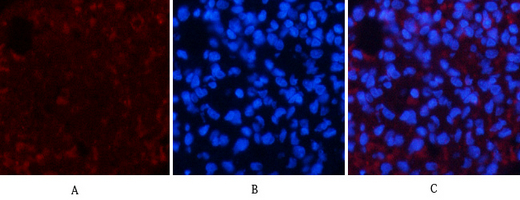
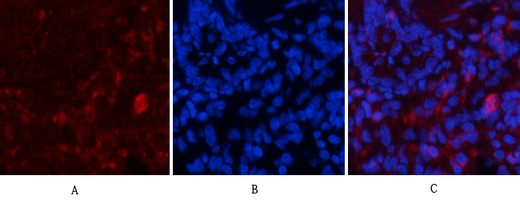
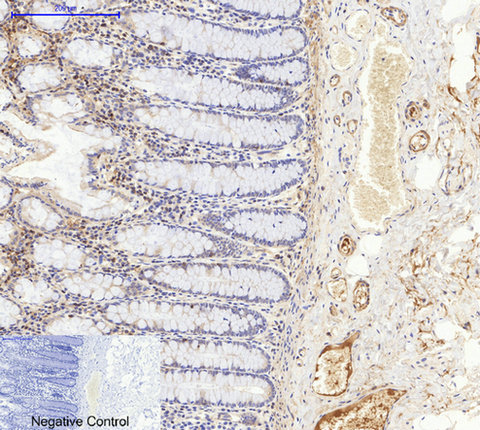
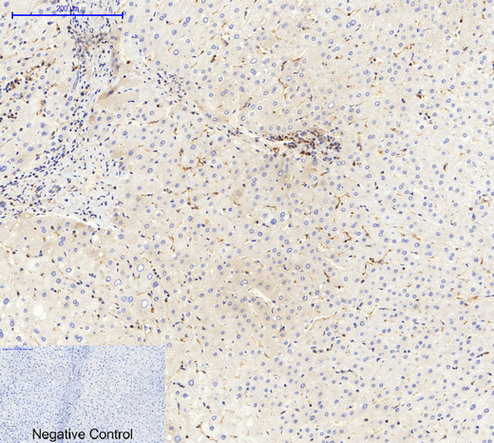
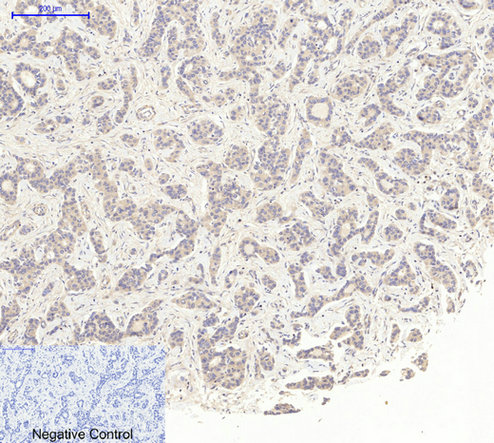
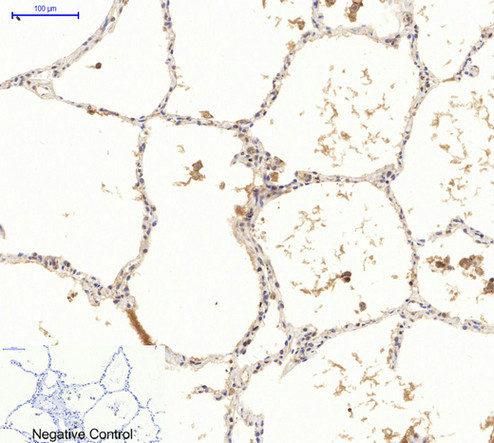
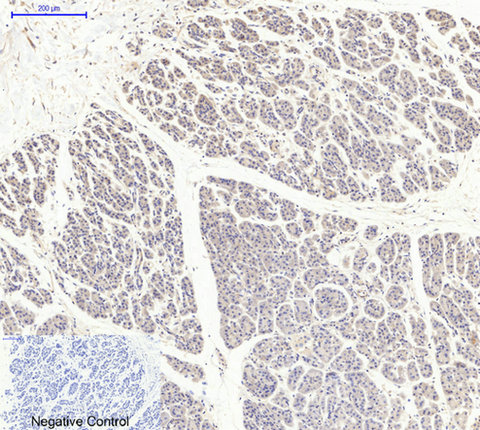
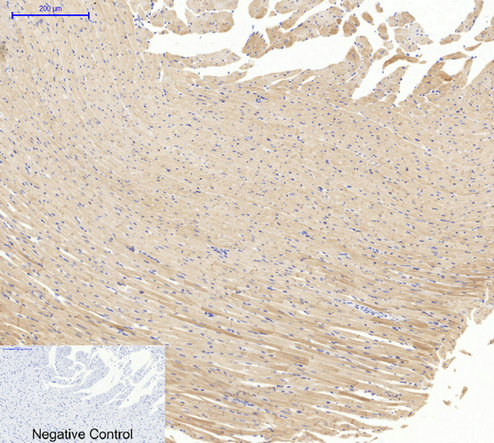
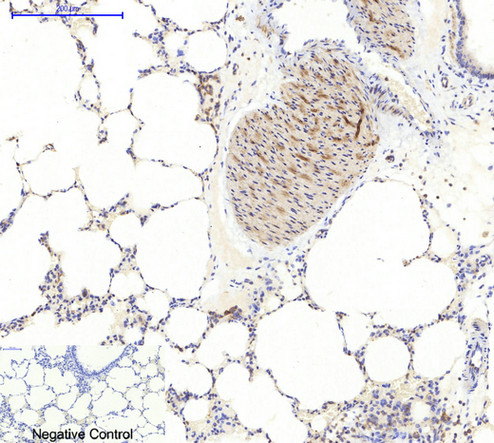
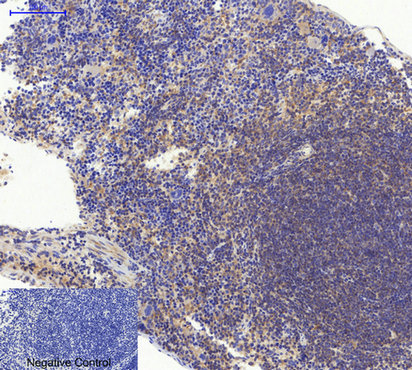
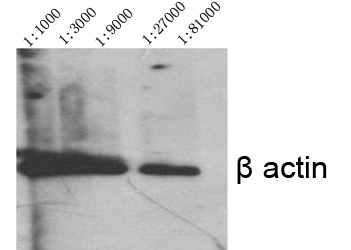
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P60709 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 41737 Da |
| Gene ID | 60 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | ACTB; Actin; cytoplasmic 1; Beta-actin |
| Dilution | IF~~IF: 1:50-200 Western Blot: 1/1000 - 1/4000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | ACTB |
|---|---|
| Function | Actin is a highly conserved protein that polymerizes to produce filaments that form cross-linked networks in the cytoplasm of cells (PubMed:25255767, PubMed:29581253). Actin exists in both monomeric (G-actin) and polymeric (F-actin) forms, both forms playing key functions, such as cell motility and contraction (PubMed:29581253). In addition to their role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, G- and F- actin also localize in the nucleus, and regulate gene transcription and motility and repair of damaged DNA (PubMed:29925947). Part of the ACTR1A/ACTB filament around which the dynactin complex is built. The dynactin multiprotein complex activates the molecular motor dynein for ultra-processive transport along microtubules (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Nucleus Note=Localized in cytoplasmic mRNP granules containing untranslated mRNAs. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Actin is a highly conserved protein that polymerizes to produce filaments that form cross-linked networks in the cytoplasm of cells (PubMed:29581253). Actin exists in both monomeric (G- actin) and polymeric (F-actin) forms, both forms playing key functions, such as cell motility and contraction (PubMed:29581253). In addition to their role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, G- and F-actin also localize in the nucleus, and regulate gene transcription and motility and repair of damaged DNA (PubMed:29925947).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.







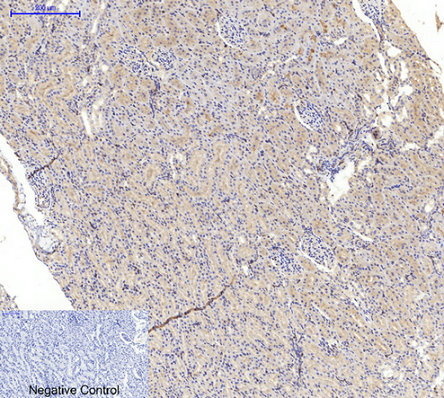
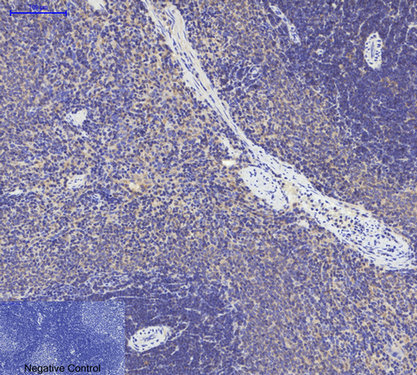
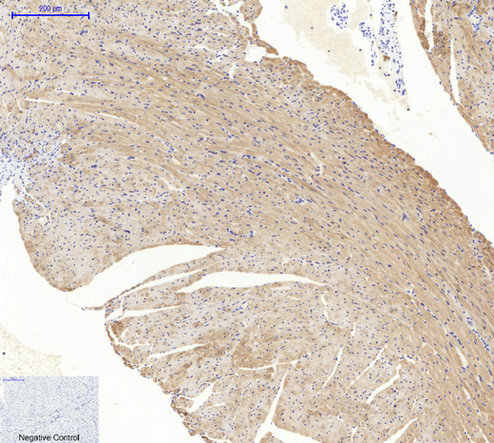
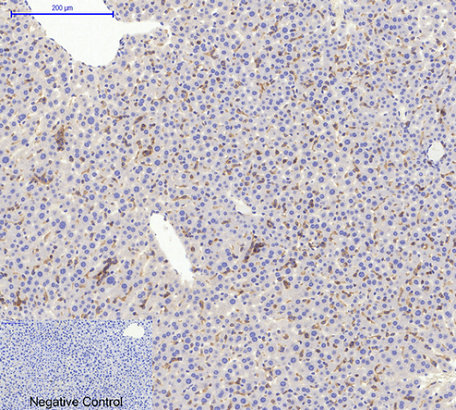


.jpg)