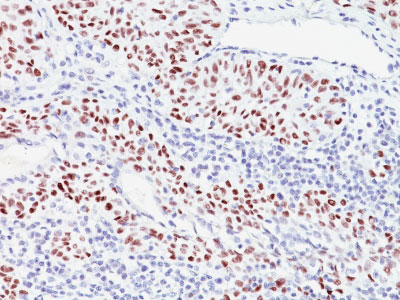
p57Kip2 (Mitotic Inhibitor/Suppressor Protein) Antibody - With BSA and Azide
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone 57P06 ]
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P49918 |
| Other Accession | 1028, 106070 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b, kappa |
| Clone Names | 57P06 |
| Calculated MW | 57kDa |
| Gene ID | 1028 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C, Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57, p57Kip2, CDKN1C, KIP2 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | p57Kip2 (Mitotic Inhibitor/Suppressor Protein) Antibody - With BSA and Azide is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CDKN1C |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KIP2 |
| Function | Potent tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/CDK complexes (cyclin E-CDK2, cyclin D2-CDK4, and cyclin A-CDK2) and, to lesser extent, of the mitotic cyclin B-CDC2. Negative regulator of cell proliferation. May play a role in maintenance of the non-proliferative state throughout life. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the heart, brain, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas and testis. Expressed in the eye. High levels are seen in the placenta while low levels are seen in the liver |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Recognizes a protein of 57kDa, identified as p57Kip2. It shows no cross-reaction with p27Kip1. p57Kip2 is a potent tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin complexes, and is a negative regulator of cell proliferation. Anti-p57 has been used as an aide in identification of complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) (no nuclear labeling of cytotrophoblasts and stromal cells) from partial hydatidiform mole (PHM) in which both cytotrophoblasts and stromal cells stain. The histological differentiation of complete mole, partial mole, and hydropic spontaneous abortion is problematic. Most complete hydatidiform moles are diploid, whereas most partial moles are triploid. Ploidy studies will identify partial moles, but will not differentiate complete moles from non-molar gestations. Complete moles carry a high risk of persistent disease and choriocarcinoma, while partial moles have a very low risk. In normal placenta, many cytotrophoblast nuclei and stromal cells are labeled with this antibody. Similar findings apply to PHM and hydropic abortus tissues. Intervillous trophoblastic islands (IVTIs) demonstrate nuclear labeling in all three entities and serve as an internal control.
References
Lee, M.-H., et al. 1995. Cloning of p57, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev. 9: 639-649. |
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.