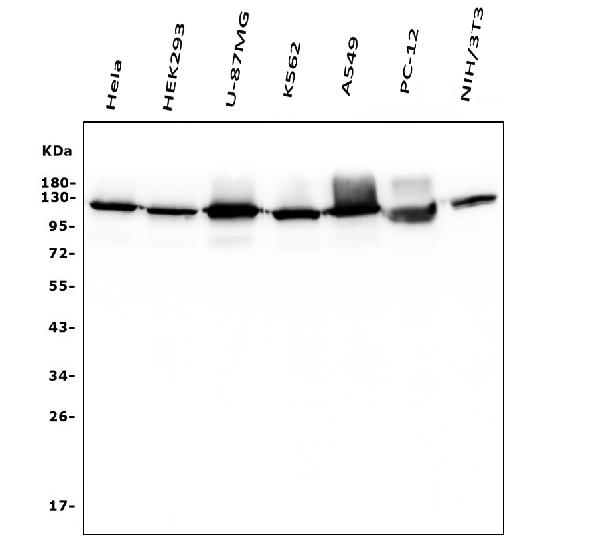
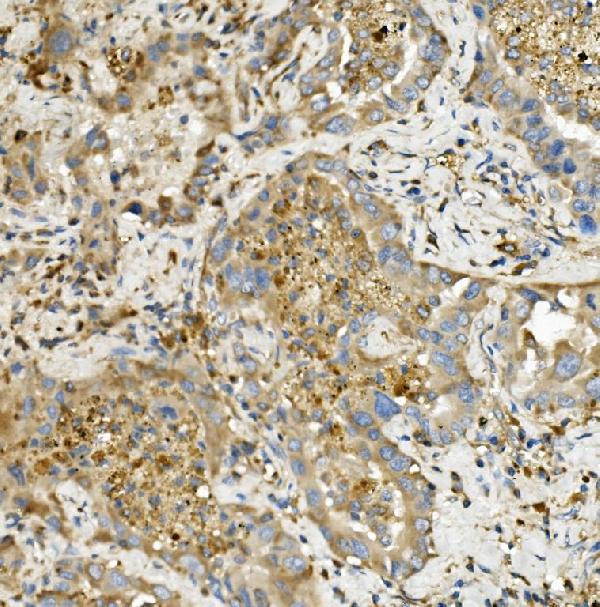
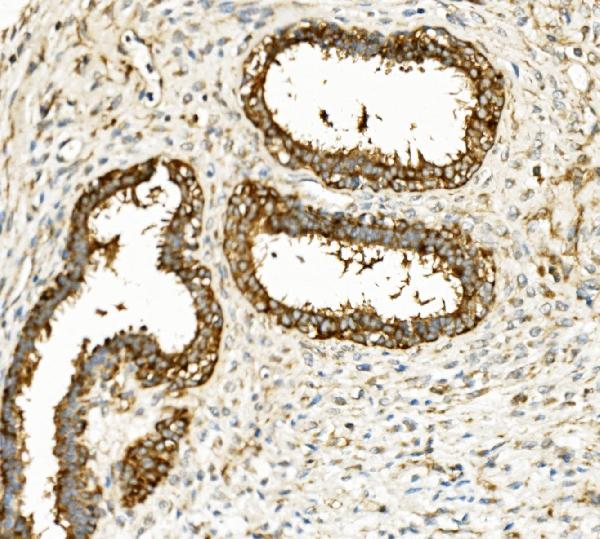
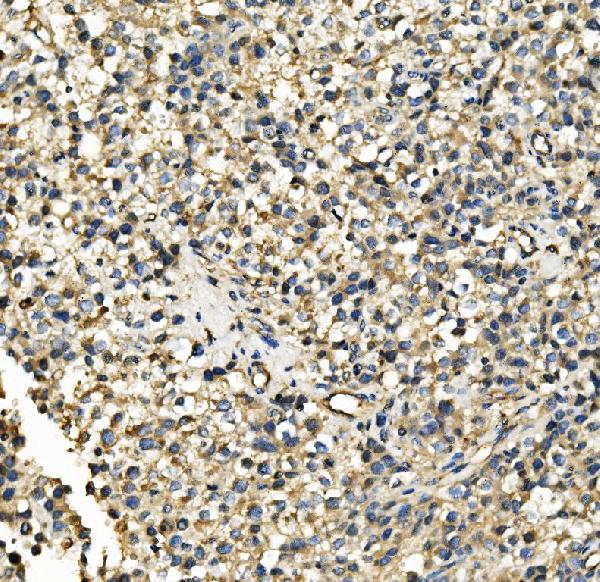
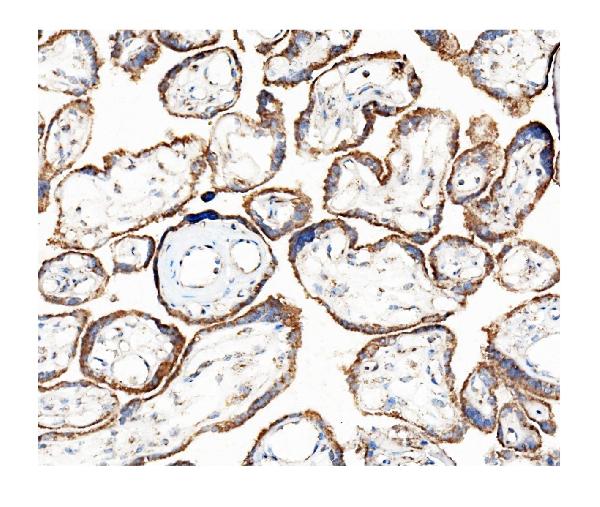
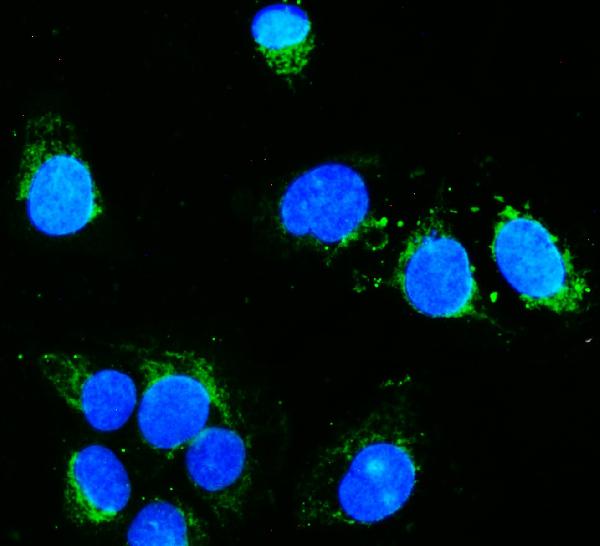
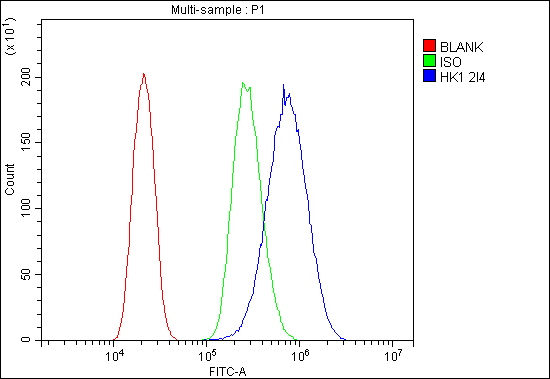
Anti-Hexokinase 1/HK1 Antibody Picoband™ (monoclonal, 2I4)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, IHC-F, IF, ICC, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P19367 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Anti-Hexokinase 1/HK1 Antibody Picoband™ (monoclonal, 2I4) . Tested in Flow Cytometry, IF, IHC, IHC-F, ICC, WB applications. This antibody reacts with Human, Mouse, Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 3098 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Hexokinase-1, 2.7.1.1, Brain form hexokinase, Hexokinase type I, HK I, Hexokinase-A, HK1 (HGNC:4922) |
| Calculated MW | 120 kDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, Mouse, Rat Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml, Human Immunohistochemistry (Frozen Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml, Human Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence, 2 µg/ml, Human Immunofluorescence, 2 µg/ml, Human Flow Cytometry, 1-3 µg/1x10^6 cells, Human |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytosol. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Peripheral membrane protein. |
| Contents | Each vial contains 4mg Trehalose, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Clone Names | Clone: 2I4 |
| Immunogen | E.coli-derived human Hexokinase 1/HK1 recombinant protein (Position: D17-R323). |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross-reactivity with other proteins. |
| Storage | Store at -20˚C for one year from date of receipt. After reconstitution, at 4˚C for one month. It can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for six months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Name | HK1 (HGNC:4922) |
|---|---|
| Function | Catalyzes the phosphorylation of various hexoses, such as D- glucose, D-glucosamine, D-fructose, D-mannose and 2-deoxy-D-glucose, to hexose 6-phosphate (D-glucose 6-phosphate, D-glucosamine 6-phosphate, D-fructose 6-phosphate, D-mannose 6-phosphate and 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6- phosphate, respectively) (PubMed:1637300, PubMed:25316723, PubMed:27374331). Does not phosphorylate N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (PubMed:27374331). Mediates the initial step of glycolysis by catalyzing phosphorylation of D-glucose to D-glucose 6-phosphate (By similarity). Involved in innate immunity and inflammation by acting as a pattern recognition receptor for bacterial peptidoglycan (PubMed:27374331). When released in the cytosol, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine component of bacterial peptidoglycan inhibits the hexokinase activity of HK1 and causes its dissociation from mitochondrial outer membrane, thereby activating the NLRP3 inflammasome (PubMed:27374331). |
| Cellular Location | Mitochondrion outer membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Note=The mitochondrial-binding peptide (MBP) region promotes association with the mitochondrial outer membrane (Probable). Dissociates from the mitochondrial outer membrane following inhibition by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, leading to relocation to the cytosol (PubMed:27374331). |
| Tissue Location | Isoform 2: Erythrocyte specific (Ref.6). Isoform 3: Testis-specific (PubMed:10978502). Isoform 4: Testis-specific (PubMed:10978502). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10978502, ECO:0000269|Ref.6} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Hexokinase-1 (HK1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HK1 gene on chromosome 10. It is mapped to 10q22.1. Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate, the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes a ubiquitous form of hexokinase which localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hemolytic anemia due to hexokinase deficiency. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants which encode different isoforms, some of which are tissue-specific.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.