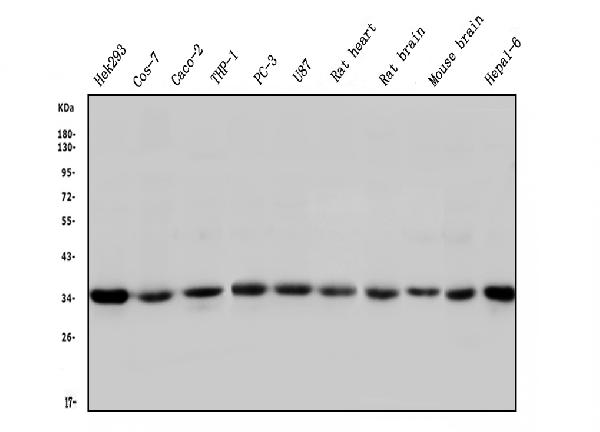
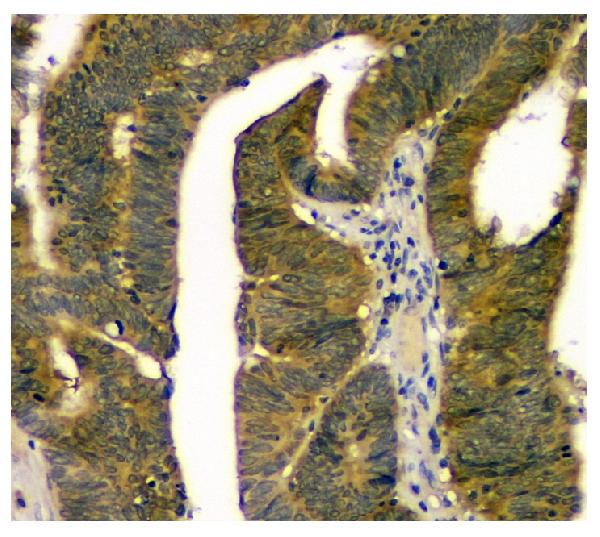
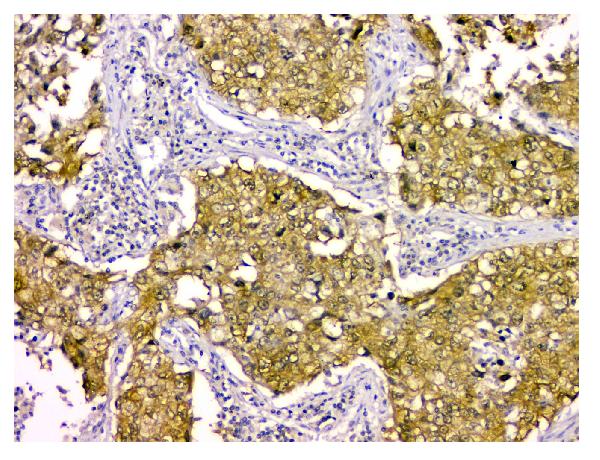
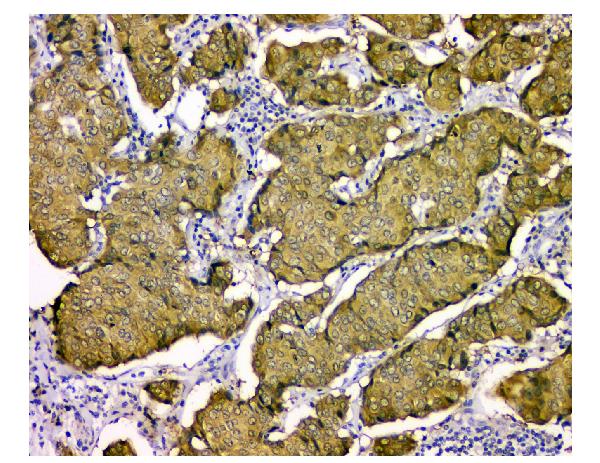
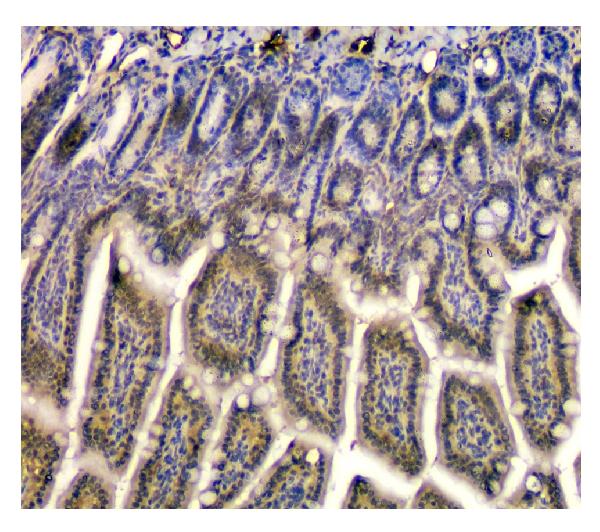
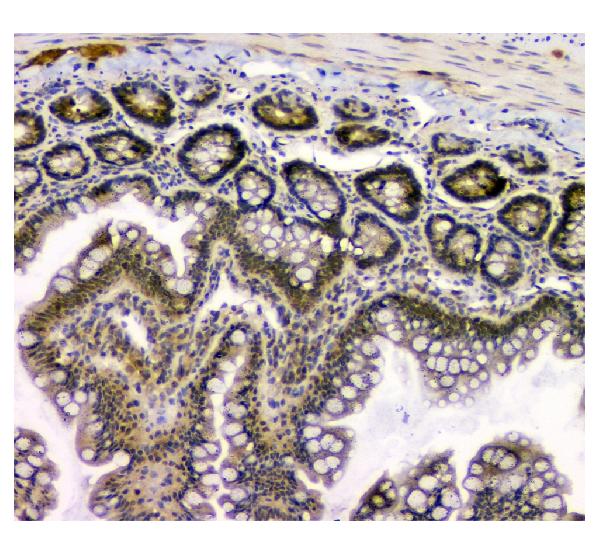
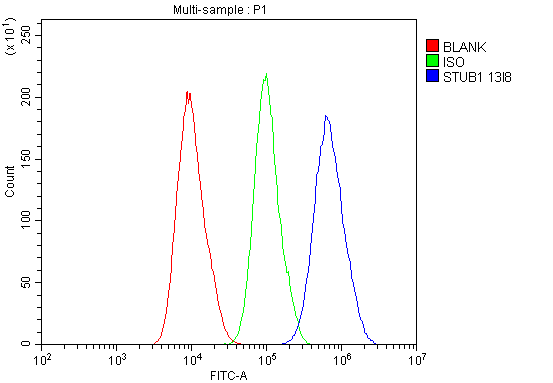
Anti-STUB1 Antibody Picoband™ (monoclonal, 13I8)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UNE7 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse, Monkey |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Anti-STUB1 Antibody Picoband™ (monoclonal, 13I8) . Tested in Flow Cytometry, IHC, WB applications. This antibody reacts with Human, Monkey, Mouse, Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500 µg/ml. |
| Gene ID | 10273 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CHIP, 2.3.2.27, Antigen NY-CO-7, CLL-associated antigen KW-8, Carboxy terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase CHIP, STIP1 homology and U box-containing protein 1 {ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11427}, STUB1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:23973223, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11427} |
| Calculated MW | 35 kDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml Flow Cytometry, 1-3 µg/1x10^6 cells |
| Subcellular Localization | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in differentiated myotubes (at protein level). Highly expressed in skeletal muscle, heart, pancreas, brain and placenta. Detected in kidney, liver and lung. |
| Contents | E. coli-derived human STUB1 recombinant protein (Position: R51-Y303). Human STUB1 shares 98% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with both mouse and rat STUB1. |
| Clone Names | Clone: 13I8 |
| Immunogen | E.coli-derived human STUB1 recombinant protein (Position: R51-Y303). |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross-reactivity with other proteins. |
| Storage | Store at -20˚C for one year from date of receipt. After reconstitution, at 4˚C for one month. It can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for six months. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Name | STUB1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:23973223, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:11427} |
|---|---|
| Function | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which targets misfolded chaperone substrates towards proteasomal degradation (PubMed:10330192, PubMed:11146632, PubMed:11557750, PubMed:23990462, PubMed:26265139). Plays a role in the maintenance of mitochondrial morphology and promotes mitophagic removal of dysfunctional mitochondria; thereby acts as a protector against apoptosis in response to cellular stress (By similarity). Negatively regulates vascular smooth muscle contraction, via degradation of the transcriptional activator MYOCD and subsequent loss of transcription of genes involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction (By similarity). Promotes survival and proliferation of cardiac smooth muscle cells via ubiquitination and degradation of FOXO1, resulting in subsequent repression of FOXO1-mediated transcription of pro-apoptotic genes (PubMed:19483080). Ubiquitinates ICER-type isoforms of CREM and targets them for proteasomal degradation, thereby acts as a positive effector of MAPK/ERK-mediated inhibition of apoptosis in cardiomyocytes (PubMed:20724525). Inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and hypertrophy in cardiomyocytes, via ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of NFATC3 (PubMed:30980393). Collaborates with ATXN3 in the degradation of misfolded chaperone substrates: ATXN3 restricting the length of ubiquitin chain attached to STUB1/CHIP substrates and preventing further chain extension (PubMed:10330192, PubMed:11146632, PubMed:11557750, PubMed:23990462). Ubiquitinates NOS1 in concert with Hsp70 and Hsp40 (PubMed:15466472). Modulates the activity of several chaperone complexes, including Hsp70, Hsc70 and Hsp90 (PubMed:10330192, PubMed:11146632, PubMed:15466472). Ubiquitinates CHRNA3 targeting it for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in cortical neurons, as part of the STUB1-VCP-UBXN2A complex (PubMed:26265139). Ubiquitinates and promotes ESR1 proteasomal degradation in response to age-related circulating estradiol (17-beta-estradiol/E2) decline, thereby promotes neuronal apoptosis in response to ischemic reperfusion injury (By similarity). Mediates transfer of non-canonical short ubiquitin chains to HSPA8 that have no effect on HSPA8 degradation (PubMed:11557750, PubMed:23990462). Mediates polyubiquitination of DNA polymerase beta (POLB) at 'Lys-41', 'Lys-61' and 'Lys-81', thereby playing a role in base-excision repair: catalyzes polyubiquitination by amplifying the HUWE1/ARF-BP1-dependent monoubiquitination and leading to POLB-degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:19713937). Mediates polyubiquitination of CYP3A4 (PubMed:19103148). Ubiquitinates EPHA2 and may regulate the receptor stability and activity through proteasomal degradation (PubMed:19567782). Acts as a co-chaperone for HSPA1A and HSPA1B chaperone proteins and promotes ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation (PubMed:27708256). Negatively regulates the suppressive function of regulatory T-cells (Treg) during inflammation by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of FOXP3 in a HSPA1A/B-dependent manner (PubMed:23973223). Catalyzes monoubiquitination of SIRT6, preventing its degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:24043303). Likely mediates polyubiquitination and down-regulates plasma membrane expression of PD-L1/CD274, an immune inhibitory ligand critical for immune tolerance to self and antitumor immunity (PubMed:28813410). Negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling by modulating the basal level of SMAD3 via ubiquitin-mediated degradation (PubMed:24613385). Plays a role in the degradation of TP53 (PubMed:26634371). Mediates ubiquitination of RIPK3 leading to its subsequent proteasome-dependent degradation (PubMed:29883609). May regulate myosin assembly in striated muscles together with UBE4B and VCP/p97 by targeting myosin chaperone UNC45B for proteasomal degradation (PubMed:17369820). Ubiquitinates PPARG in macrophages playing a role in M2 macrophages polarization and angiogenesis (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A6HD62}. Note=Translocates to the nucleus in response to inflammatory signals in regulatory T-cells (Treg) Localizes to mitochondria following oxygen and glucose deprivation- induced cellular stress (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A6HD62, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23973223} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in differentiated myotubes (at protein level) (PubMed:17369820). Highly expressed in skeletal muscle, heart, pancreas, brain and placenta (PubMed:10330192, PubMed:11435423) Detected in kidney, liver and lung (PubMed:10330192, PubMed:11435423) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
STUB1 (STIP1 homology and U-Box containing protein 1), also known as CHIP (C terminus of HSC70-Interacting Protein), is a human gene. This gene encodes a protein containing tetratricopeptide repeat and a U-box that functions as a ubiquitin ligase/cochaperone. The encoded protein binds to and ubiquitinates shock cognate 71 kDa protein (Hspa8) and DNA polymerase beta (Polb), among other targets. Mutations in this gene cause spinocerebellar ataxia, autosomal recessive 16. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. There is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 2.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.