Anti-Lin28 LIN28A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IP, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H9Z2 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Format | Liquid |
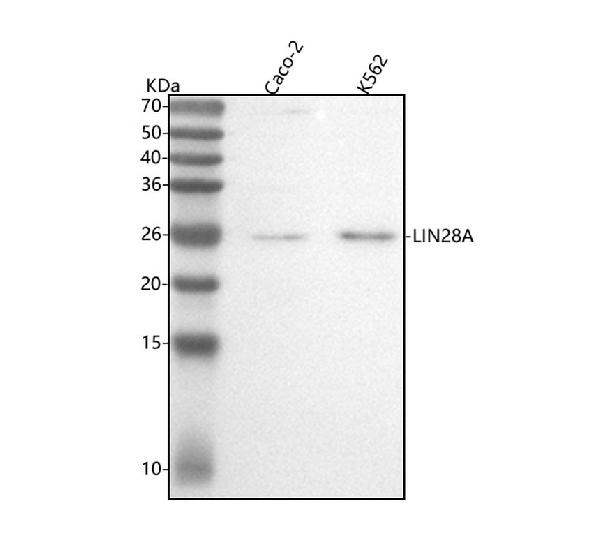
| Description | Anti-Lin28 LIN28A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody . Tested in WB, IP, Flow Cytometry applications. This antibody reacts with Human. |
| Gene ID | 79727 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein lin-28 homolog A, Lin-28A, Zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 1, LIN28A, CSDD1, LIN28, ZCCHC1 |
| Calculated MW | 22743 MW KDa |
| Application Details | WB 1:500-1:2000 IP 1:50 FC 1:50 |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm. Nucleus, nucleolus. Predominantly cytoplasmic (PubMed:22118463). Nucleolar localization observed in 10-15% of the nuclei in differentiated myotubes (By similarity). Shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Localizes to cytoplasmic processing bodies and stress granules.. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in embryonic stem cells, placenta and testis. Tends to be up-regulated in HER2-overexpressing breast tumors.. |
| Contents | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, 0.4-0.5mg/ml BSA. |
| Clone Names | Clone: AAAG-12 |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Lin28 |
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Storage | Store at -20°C for one year. For short term storage and frequent use, store at 4°C for up to one month. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Name | LIN28A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CSDD1, LIN28, ZCCHC1 |
| Function | RNA-binding protein that inhibits processing of pre-let-7 miRNAs and regulates translation of mRNAs that control developmental timing, pluripotency and metabolism (PubMed:21247876). Seems to recognize a common structural G-quartet (G4) feature in its miRNA and mRNA targets (Probable). 'Translational enhancer' that drives specific mRNAs to polysomes and increases the efficiency of protein synthesis. Its association with the translational machinery and target mRNAs results in an increased number of initiation events per molecule of mRNA and, indirectly, in mRNA stabilization. Binds IGF2 mRNA, MYOD1 mRNA, ARBP/36B4 ribosomal protein mRNA and its own mRNA. Essential for skeletal muscle differentiation program through the translational up- regulation of IGF2 expression. Suppressor of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis, including that of let-7, miR107, miR-143 and miR-200c. Specifically binds the miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs), recognizing an 5'-GGAG-3' motif found in pre-miRNA terminal loop, and recruits TUT4 and TUT7 uridylyltransferases (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). This results in the terminal uridylation of target pre-miRNAs (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). Uridylated pre-miRNAs fail to be processed by Dicer and undergo degradation. The repression of let-7 expression is required for normal development and contributes to maintain the pluripotent state by preventing let-7-mediated differentiation of embryonic stem cells (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). Localized to the periendoplasmic reticulum area, binds to a large number of spliced mRNAs and inhibits the translation of mRNAs destined for the ER, reducing the synthesis of transmembrane proteins, ER or Golgi lumen proteins, and secretory proteins. Binds to and enhances the translation of mRNAs for several metabolic enzymes, such as PFKP, PDHA1 or SDHA, increasing glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Which, with the let-7 repression may enhance tissue repair in adult tissue (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Rough endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3}. Cytoplasm, P-body. Cytoplasm, Stress granule. Nucleus, nucleolus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3}. Note=Predominantly cytoplasmic (PubMed:22118463). In the cytoplasm, localizes to peri-endoplasmic reticulum regions and detected in the microsomal fraction derived from rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) following subcellular fractionation May be bound to the cytosolic surface of RER on which ER-associated mRNAs are translated (By similarity). Shuttle from the nucleus to the cytoplasm requires RNA-binding (PubMed:17617744). Nucleolar localization is observed in 10-15% of the nuclei in differentiated myotubes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17617744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22118463} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in embryonic stem cells, placenta and testis. Tends to be up-regulated in HER2-overexpressing breast tumors |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.