Anti-NSF Picoband Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P46459 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
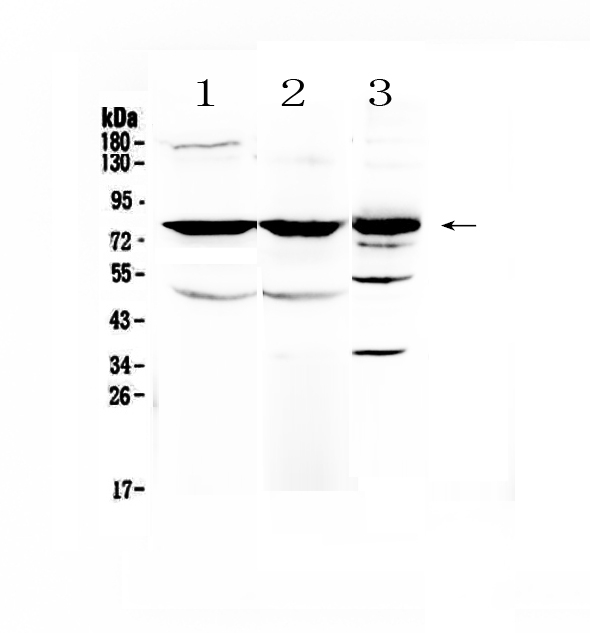
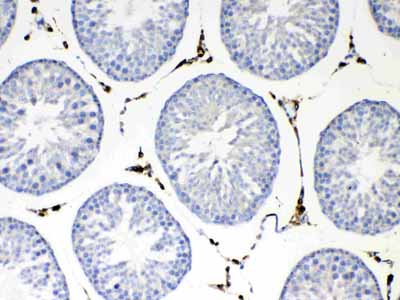
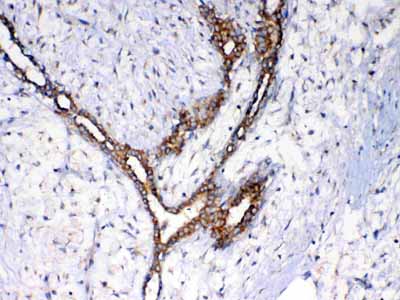
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for NSF detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P, Direct ELISA in Human;Mouse;Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 4905 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Vesicle-fusing ATPase, 3.6.4.6, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein, NEM-sensitive fusion protein, Vesicular-fusion protein NSF, NSF |
| Calculated MW | 82594 Da |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml Immunohistochemistry(Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml Direct ELISA, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm. |
| Contents | Each vial contains 4mg Trehalose, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | E. coli-derived human NSF recombinant protein (Position: N620-D744). |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins. |
| Storage | At -20˚C; for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C; for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C; for a longer time. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | NSF |
|---|---|
| Function | Required for vesicle-mediated transport. Catalyzes the fusion of transport vesicles within the Golgi cisternae. Is also required for transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi stack. Seems to function as a fusion protein required for the delivery of cargo proteins to all compartments of the Golgi stack independent of vesicle origin. Interaction with AMPAR subunit GRIA2 leads to influence GRIA2 membrane cycling (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor, also known as NSF, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the NSF gene. NSF is a homohexameric AAA ATPase involved in membrane fusion. NSF is ubiquitously found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is a central component of the cellular machinery in the transfer of membrane vesicles from one membrane compartment to another. During this process, SNARE proteins on two joining membranes (usually a vesicle and a target membrane such as the plasma membrane) form a tight complex. This aids fusion of the vesicle with the target membrane. It has been proposed that the role of NSF is to undo these SNARE complexes once membrane fusion has occurred, using the hydrolysis of ATP as an energy source, allowing the dissociated SNAREs to be recycled for reuse in further rounds of membrane fusion. This proposal remains controversial, however. Recent work indicates that the ATPase function of NSF does not function in recycling of vesicles but rather functions in the act of fusing vesicles with the plasma membrane.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.