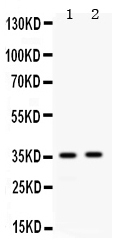
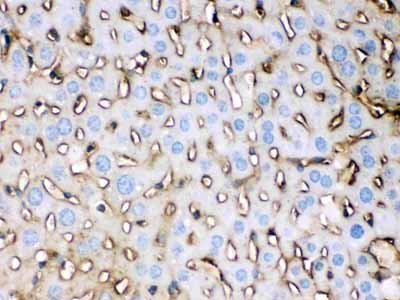
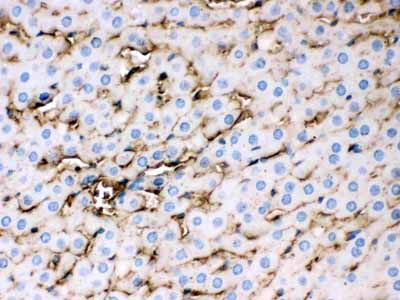
Anti-APOE Picoband Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P08226 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Apolipoprotein E(APOE) detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P in Mouse;Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 11816 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Apolipoprotein E, Apo-E, Apoe |
| Calculated MW | 35867 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Immunohistochemistry(Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml, Mouse, Rat, By Heat Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Mouse |
| Subcellular Localization | Secreted . |
| Tissue Specificity | Secreted in plasma. |
| Protein Name | Apolipoprotein E |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | E.coli-derived mouse Apolipoprotein E recombinant protein (Position: D55-Q294). Mouse Apolipoprotein E shares 75% and 94.6% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with human and rat Apolipoprotein E, respectively. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | Apoe |
|---|---|
| Function | APOE is an apolipoprotein, a protein associating with lipid particles, that mainly functions in lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids. APOE is a core component of plasma lipoproteins and is involved in their production, conversion and clearance. Apolipoproteins are amphipathic molecules that interact both with lipids of the lipoprotein particle core and the aqueous environment of the plasma. As such, APOE associates with chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) but shows a preferential binding to high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It also binds a wide range of cellular receptors including the LDL receptor/LDLR and the very low-density lipoprotein receptor/VLDLR that mediate the cellular uptake of the APOE-containing lipoprotein particles (By similarity). Finally, APOE has also a heparin-binding activity and binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the surface of cells, a property that supports the capture and the receptor-mediated uptake of APOE-containing lipoproteins by cells (PubMed:23676495). |
| Cellular Location | Secreted {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649}. Secreted, extracellular space {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649}. Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649}. Extracellular vesicle {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649}. Endosome, multivesicular body {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649}. Note=In the plasma, APOE is associated with chylomicrons, chylomicrons remnants, VLDL, LDL and HDL lipoproteins. Lipid poor oligomeric APOE is associated with the extracellular matrix in a calcium- and heparan-sulfate proteoglycans- dependent manner. Lipidation induces the release from the extracellular matrix. Colocalizes with CD63 and PMEL at exosomes and in intraluminal vesicles within multivesicular endosomes {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02649} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
APOE is also known as AD2 or LPG. The protein encoded by this gene is a major apoprotein of the chylomicron. It binds to a specific liver and peripheral cell receptor, and is essential for the normal catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. This gene maps to chromosome 19 in a cluster with the related apolipoprotein C1 and C2 genes. Mutations in this gene result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, or type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron and VLDL remnants. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.